COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








In 2009, Ryan Dahl introduced Node js to solve a problem that traditional web servers couldn't handle. The then-existing tech stack was not efficient enough to handle a concurrent stream of requests smoothly.
Ryan created a JavaScript-based runtime - Node.js. As a result, JavaScript was already a standard language in the front end and, with the arrival of NodeJS, reached the server-side, too. The JavaScript on both sides was not a major reason behind the success of Nodejs, but its ability to handle a large number of concurrent requests was.
Till 2025, it is running behind 4.7% of all the websites, W3tech reports. Node.js supports applications from payments to space missions. This article explores how 10 companies using Nodejs in 2025.
Netflix, a multinational streaming giant with more than 130 million subscribers, generates billions of streaming hours every week. Heavy use of a Java-based backend served Netflix well for a while.
However, the team soon learned that the architecture would become a bottleneck as subscriber numbers increased. So, Netflix's engineering team began searching for alternatives. They needed a technology that had a faster startup time and could handle more concurrent requests. They made a selection and landed on Node.js.
By integrating Node.js as one of their core technologies, Netflix observed about a 70% reduction in startup times.

With Node.js, Netflix could use JavaScript on both the frontend and backend. This eliminated the need for developers to context-switch between different languages.
Node.js's lightweight nature and modular design made it a perfect fit for Netflix's evolving microservices architecture.
Similar to Netflix, PayPal made a switch to Node.js in 2013, moving from a Java tech stack to normalize their development process. PayPal faced a dilemma in their development process because they were divided between their technology stack. The backend of their products and systems was primarily in Java, while the frontend was JavaScript. With developers switching contexts and languages often, it was causing a drain on efficiency.
PayPal's effects of using JavaScript on both the frontend and backend were positive.
As Jeff Harrell, Director of Engineering at PayPal, said in a PayPal Tech Blog post titled "Node.js at PayPal," published on November 22, 2013:
"Node.js helps us solve this by enabling both the browser and server applications to be written in JavaScript. It unifies our engineering specialties into one team, which allows us to understand and react to our users' needs at any level in the technology stack."
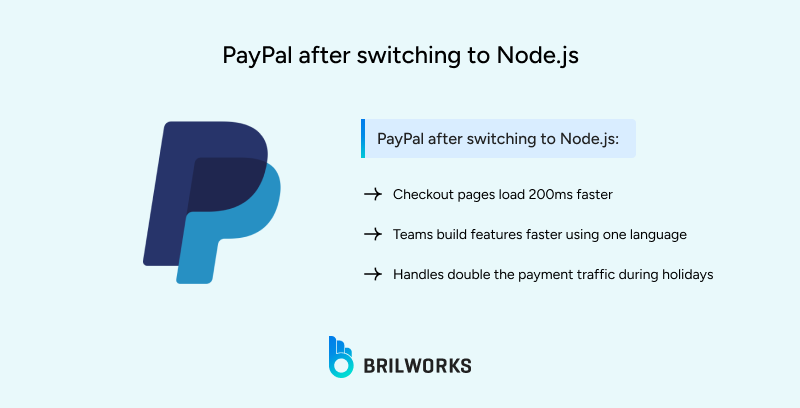
Measurable positive effects of this decision were:
Reduced Development Time
Reduction in checkout page load times
35% decrease in the average response time
Increased Transaction Handling Capacity:
Node.js improved PayPal's system:
Unified code for team efficiency.
Faster transaction processing.
Higher capacity for traffic spikes.
It was another company that included NodeJS in its tech stack, which had earlier relied on a Java-based backend. To serve its 80 million monthly users, Walmart decided to leverage Node.js capabilities to handle immense traffic. This move was part of a larger overall strategy of becoming faster and more distributed.
With this new architecture incorporating Nodejs as one of the key technologies, the company could handle thousands of concurrent requests with ease on a single thread.
As discussed in various articles about how Walmart evolved, especially with the attention paid to their 2013 Black Friday, Node.js was critical. Walmart servers processed 1.5 billion requests daily on Thanksgiving weekend. 70% of the requests were served on mobile and driven on Node.js.
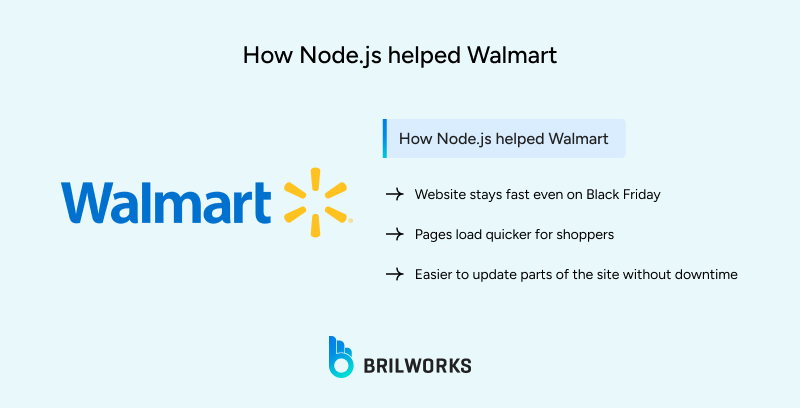
Node.js helped Walmart:
Speed up page loads for shoppers.
Support modular development for teams.
Enhance search engine rankings.
While the much-publicized struggle that Walmart has been on with retail e-commerce was their growth, LinkedIn’s struggle was different. LinkedIn wanted to create a more fluid experience for their users. The asynchronous version of Ruby on Rails that LinkedIn used just didn't seem to work with their backend as expected.
The Ruby on Rails-powered structure was not enough for like job search, profile updates, and notifications. It was good for development velocity, but it wasn't built for a mobile application of this size with enough concurrency and low latency.
To address these limitations and provide a truly fluid mobile experience, LinkedIn made the strategic decision to adopt Node.js for its mobile backend. A senior software engineer at LinkedIn, in a technical post, highlighted the advantages they had upon Node.js adoption.

Reduced latency.
Much better performance
Lower memory overhead
20x faster performance in some scenarios
Backend mobile teams combined into a single unit
Servers were cut to 3 from 30
Similar to PayPal, LinkedIn's move to Node.js allowed them to use JavaScript across their entire stack for the mobile application, from the frontend (mobile app UI) to the backend. This eliminated the need for developers to context-switch between Ruby and JavaScript.
Faster mobile response times.
Unified code for quicker development.
Scalable system for traffic growth.
A water leak in an astronaut's spacesuit during a spacewalk in 2013 revealed a critical weakness in NASA's then-current data infrastructure. The issues were linked to its data-processing architecture, in which data was scattered across different systems and databases. Data processing was a time-consuming, 28-step process. This means that to get an entire data profile involved a 28-step process.
It was inefficient, and that led NASA to work on the tech stack. The company decided to leverage Node.js as a core component in the new design system to manage the data. Here's how Node.js provided the technical solutions they needed:
The 28-step data retrieval process had significant latency built into it. Because Node.js follows an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model, it can process many concurrent data requests without stopping execution. This allowed NASA to reduce the data retrieval process from 28 different steps down to 7 steps, and therein achieved a data access speed increase of 300%.
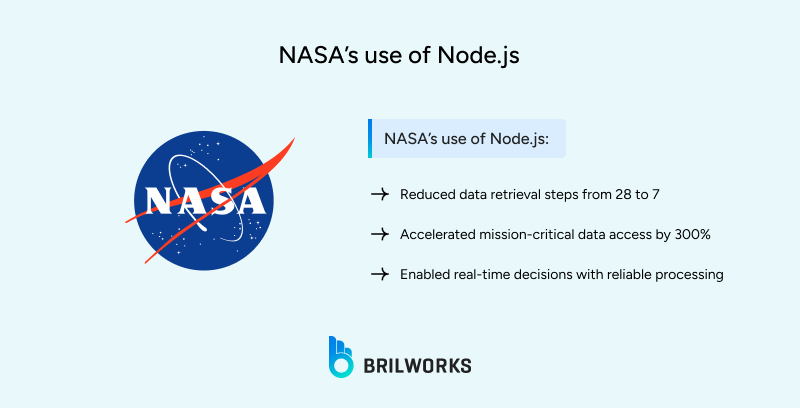
Real-time data for mission decisions.
Reliable processing for critical tasks.
Efficient server resource use.
Trello is a project management software that has over 25 million users. When the company decided to build a single-page application (SPA) with real-time synchronization across all users, Trello's developers made the decision to utilize Node.js for the back end.
Node.js has a structure that is particularly favorable for applications that need a high volume of concurrent connections.
Trello's development team specifically chose Node.js because it could handle real-time updates of single-page applications. This ensured that when a team member edited a task board item, the updates would appear in real-time for the other colleagues who are using the task board, offering optimal convenience for teams that are working remotely.

Instant updates for team boards.
Fast prototyping for new features.
Scalable system for user growth.
Uber's core business relies on instant, reliable connections between riders and drivers. Managing millions of concurrent requests, tracking real-time locations, and pushing instant updates, all in real-time, is no easy task. The company was using a Python-based monolithic architecture. With that architecture, there are some concurrency issues.
To solve those issues, Uber decided to build its critical trip execution engine using Nodejs, a key technology within its evolving microservices architecture. Node.js was chosen specifically for its strengths in handling the high-volume, real-time, and I/O-intensive demands of their marketplace.

Real-time tracking for riders.
Flexible microservices for systems.
High capacity for request spikes.
Medium, with 25 million users, uses Node.js with NGINX to deliver articles quickly and streamline content updates for its publishing platform. Medium's developers found Node.js reduced deployment times by 15 minutes and achieved 2.7-second page loads. This allowed writers to publish stories faster and readers to access them without delays, boosting engagement on topics like technology trends.
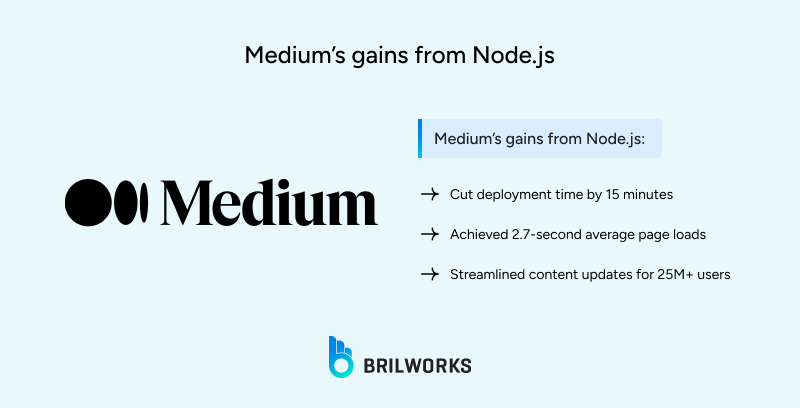
Faster content updates for writers.
Quick page loads for readers.
Unified code for efficiency.
Yahoo, adopting Node.js in 2009, uses it for 75% of its web applications, scaling single-page apps for its users. As an early adopter, Yahoo started using Node.js for backend tasks like file uploads before expanding it to frontend apps. This improved performance across platforms, helping Yahoo maintain its web presence in the early 2010s.
Scalable single-page applications.
Flexible code for both stacks.
Faster app processing.
GoDaddy, which manages 77 million domains, migrated its Website Builder to be developed in Node.js from C# to improve both performance and scalability. GoDaddy developers noted in a technical update that Node.js combined with Cassandra NoSQL allowed them to simplify their Website Builder to manage millions of website domains easily.
Scalable system for domains.
Faster data processing.
Flexible tech integration.
As we've seen from the diverse challenges and triumphs of tech giants, Node.js stands as a pivotal technology for organizations demanding high performance and real-time capabilities.
From Netflix and PayPal to Trello and Uber, Node.js has proven to be a powerful tool. Node.js is consistently being chosen, time and time again, to build scalable, fast, and responsive digital experiences of all sorts.

The examples of these real-world applications reveal the versatility and power of Node.js. Now, if you're thinking about how these business leaders are using Node.js to gain unprecedented agility and efficiency, then now is the time to consider Node.js development, if your business seeks to have a similar impact. Let us show you how Node.js can change your digital infrastructure and help you launch into your next growth phase.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements