COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








As an application grows in size, developers often find themselves tracking down and fixing pesky bugs. These bugs are not always the result of poorly implemented code; they can arise due to the inherent complexity of the tasks at hand. Debugging can never be eliminated, but this process can be made less complex by using debugging tools (or debuggers).
React Native offers loads of useful features and tools to make the debugging process simpler. In this article, we will explore the tools that you can use for debugging React apps.
React Native debugging is a process of finding bugs and issues within a React program. It involves a strategy consisting of testing tools, methodologies, and standard practices for debugging a React Native program. These methods help expert React developers reduce the debugging timeline.
Here, we look at some tools and methods for debugging a React Native app effectively.
React Native comes equipped with an in-app debugging tool that includes a variety of options to help developers tackle bugs and resolve issues efficiently. You can enable these methods through the React Native Dev Menu.
To access the Dev Menu, either shake your device or use these keyboard shortcuts:
Alternatively, for Android devices and emulators, you can run the following in your terminal:
adb shell input keyevent 82
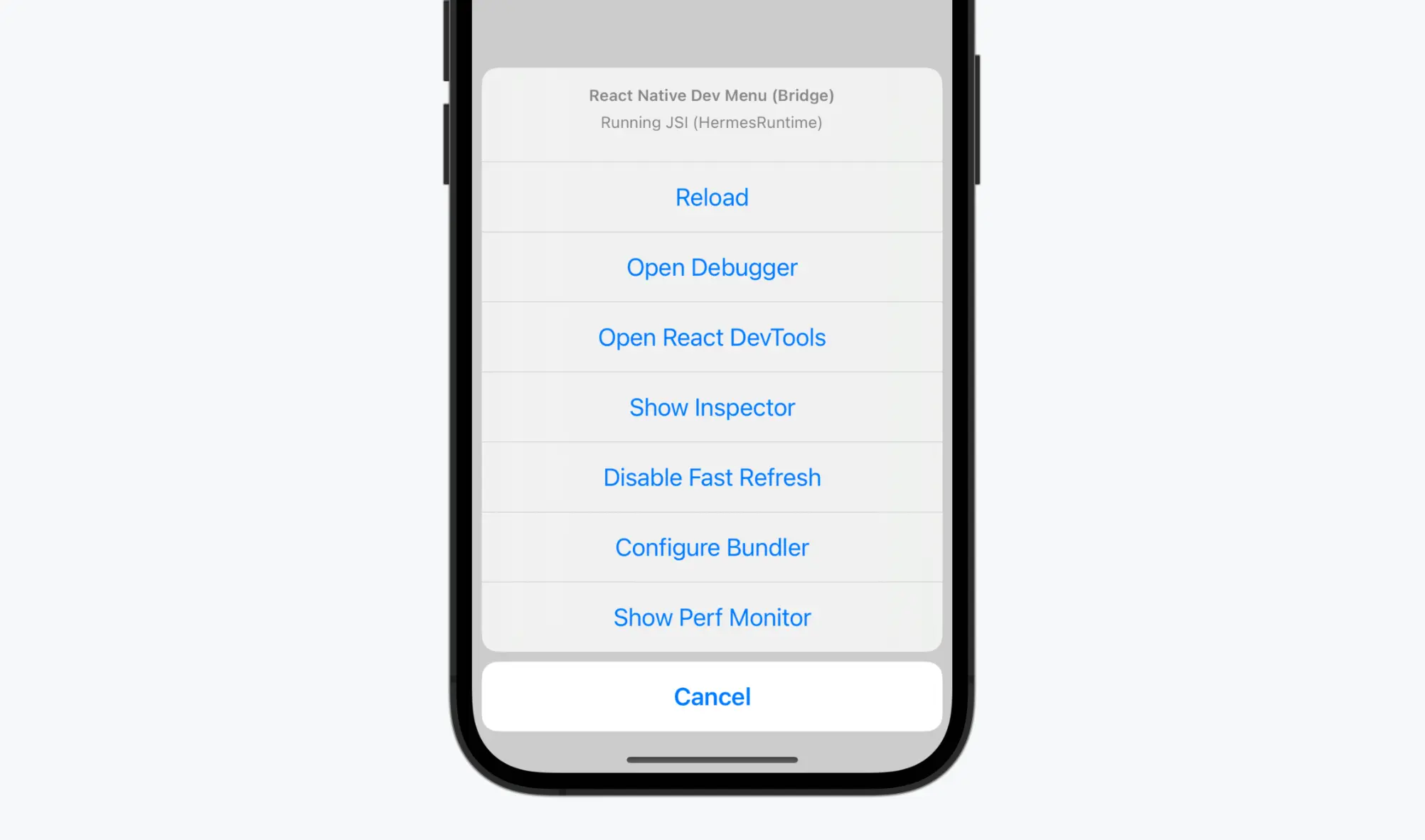
The Dev Menu gives you quick access to the following built-in options:
Note: While “Open Debugger” connects to Chrome DevTools, and “React DevTools” is often used alongside it, React DevTools is a standalone utility that is not built into React Native. We'll cover it in more detail below.
Choosing the right set of tools can drastically improve your efficiency. In this part, we’ll walk through the essential tools available for debugging React Native applications and provide practical insights into platform-specific setups.
React Native Debugger is a desktop tool that combines several debugging features into one place. Instead of switching between separate tools to inspect your app’s layout, data flow, or network calls, you can do it all from a single screen.
It connects with tools like React DevTools (for viewing component structure) and Redux DevTools (for tracking how data changes in your app). If you’re using Redux or any similar state management library, the debugger lets you watch how the data updates step by step. For example, when a user taps a button, you can see exactly what data changed as a result.
You can also:
Check how your component tree is structured and what data each part is using
Track log messages, errors, and warnings in the console
View API requests and responses in real time
To start using it:
Download React Native Debugger from GitHub
Open the debugger before you start your app
In your app, open the developer menu and enable “Remote JS Debugging”
If your project uses the Hermes engine or a custom configuration, you may need to adjust some settings for it to connect. Once it’s set up, the debugger helps you see how your app behaves—from user actions to data updates to backend responses, all in one window.
It's especially helpful when you want to trace what's happening in the app without jumping between multiple tabs or tools.
Flipper is a desktop debugging platform built by Meta. It gives you a visual interface to inspect your app's layout, view logs, monitor performance, and debug network requests. Unlike some tools that focus only on specific areas (like UI or data), Flipper supports a broader range of debugging tasks. For example:
You can inspect the structure of your React Native screens and see how styles are applied
Use the Logs tab to view real-time messages from your app
Track network activity, including outgoing API calls and server responses
It is a plugin-based system, comes with built-in features, but you can also add community plugins or build your own.
To get started:
Install Flipper and the react-native-flipper package in your app
Start Flipper before running your app
Make sure you’re using a supported React Native version (usually 0.62 and above)
If you're debugging a more complex app, especially one with both native and JavaScript parts, Flipper offers a good middle ground. It helps surface issues you might otherwise miss when relying on browser-based tools alone.
LogBox is React Native’s built-in error and warning display system, introduced in version 0.63. It replaced the older RedBox and YellowBox, offering a cleaner and more organized way to surface problems during development.
When something goes wrong:
LogBox runs automatically in development mode; there’s no need to configure it manually. But it’s not just for visual alerts. You can control what gets shown in the console:
LogBox.ignoreLogs(['Warning: ...']); // Suppress specific warnings
LogBox.ignoreAllLogs(); // Silence everything (use with caution)
If you’ve worked with web development before, you’ve probably used Chrome DevTools. React Native allows you to use this same tool to debug your app’s JavaScript code.
When you enable Remote JS Debugging in your React Native app, it opens your app’s JavaScript code inside Chrome. This gives you access to a familiar set of tools:
This setup doesn't give you full access to native code or performance metrics, but it's useful when you're tracking down logic errors, broken UI behaviors, or unexpected data issues in your JavaScript layer.
To use Chrome DevTools with React Native:
Just keep in mind: when using this method, JavaScript is run in a browser thread, not on the device. So things like performance might not behave exactly the same. Still, for logic debugging, Chrome DevTools remains one of the most accessible options.
Despite the range of tools available, console.log() remains one of the most widely used debugging techniques in React Native. It’s quick, requires no setup, and often gets you just enough insight to catch what’s going wrong.
You can use it to:
Print the value of props, states, or variables
Trace when certain parts of your code run
Log API responses or error messages
Verify conditional logic in functions
Logs appear directly in your terminal (Metro bundler output), or if you're using a debugger like Flipper or Chrome DevTools, they’ll show up there too. This makes it easy to follow how your code behaves while interacting with the app.
That said, logging does have limits. It won’t help with layout issues, native crashes, or performance bottlenecks. But it’s still the fastest way to confirm what your app is doing, especially during early development or while fixing small bugs.
For larger projects, it’s useful to structure logs with tags or use wrappers like console.warn, console.error, or even external logging libraries. That helps filter and make sense of output when things get noisy.
If your React Native app uses WebView components (for rendering web content inside your app), Safari’s Developer Tools can come in handy, especially on macOS when debugging on iOS simulators or devices.
Here’s when and why you might use it:
Your app embeds web pages via react-native-webview.
You want to inspect or debug HTML, CSS, or JavaScript running inside the WebView.
You're developing a hybrid app that blends React Native views with embedded browser views.
To use it:
Enable Web Inspector in your iOS device settings (Settings → Safari → Advanced).
Connect your device to your Mac via USB.
Open Safari → Develop menu → Select your device → Pick the WebView to inspect.
It lets you:
Inspect and edit DOM elements.
View console logs.
Debug JavaScript execution inside the WebView.
Analyze network requests made from the embedded page.
That said, Safari DevTools don’t help with native views, JavaScript bridge issues, or React component trees. It’s not a React Native debugger; it’s a web content debugger, useful in hybrid use cases.
React Developer Tools is one of the most useful browser extensions for inspecting how your React Native components behave during runtime. Once connected, it gives you a visual representation of your app’s component tree.
You can click into any component to view its current state, props, and hook values. This is particularly helpful when a UI element doesn’t behave as expected, like when a component doesn't re-render, or props don't appear to be passed correctly.
What makes this tool more than just a viewer is its built-in Profiler. It tracks component rendering performance, showing how long each component takes to render and what causes it to re-render in the first place. This kind of insight is valuable for optimizing performance and spotting unnecessary re-renders that could slow down your app.
Here’s what React Developer Tools helps you uncover:
Setting it up is relatively simple. You can install the standalone version using:
npm install -g react-devtools
Then run it using react-devtools and make sure remote debugging is enabled in your React Native environment. In some cases, especially with Expo or custom Metro servers, you may need to manually ensure it’s connecting to the right port.
For deeper performance issues, recording a few sessions in the Profiler can help you visualize exactly where your app is spending time and which parts can be optimized.
Reactotron is a desktop app that gives you a real-time look into what’s happening inside your React Native app. It’s not part of the core React Native toolkit, but many developers use it to monitor app state, API calls, performance, and more, all in one place.
Once set up, Reactotron lets you:
Inspect state and Redux stores in real time.
Track network requests, including their payloads and responses.
Monitor performance issues like long rendering times.
Log custom messages from your code using console.tron.log().
Here’s a basic usage snippet:
import Reactotron from 'reactotron-react-native';
Reactotron
.configure() // connects to localhost by default
.useReactNative()
.connect();
console.tron.log('App started');
You’ll need to install both the desktop client and the npm package in your project. For Redux users, there’s also a plugin that helps visualize store changes and dispatched actions, useful when tracking down subtle bugs in app logic.
While it’s mostly used during development, you can configure it to strip out debug code from production builds to avoid bloating your app or exposing sensitive logs.
See Also: A Guide to Animations in React Native
While the development experience is largely unified, understanding the native layers is essential when tracking down complex issues.
On iOS, Xcode remains the primary tool for debugging. It provides access to device logs, breakpoints, and native-level inspection that can be vital when dealing with build failures or Objective-C-related errors.
For developers working regularly with iOS builds, it's important to become familiar with Xcode's debugging console and instrumentation features. Apple's official documentation is a useful reference point.
Android debugging, on the other hand, typically revolves around Android Studio. It offers real-time access to Logcat, memory tools, and emulator controls. Android Studio also lets you inspect UI layouts and thread activity.
Google's documentation offers extensive guidance on using these tools effectively.
When testing apps on physical devices, extra configuration may be necessary to enable remote debugging. For Android, you can use the adb reverse command to set up port forwarding so your app can communicate with the Metro bundler:
adb reverse tcp:8081 tcp:8081
If needed, you can also update the debug server host manually through the Dev Menu by entering your computer’s IP address.
On iOS, debugging on a real device usually requires a change to the default WebSocket configuration. You will need to update the IP address inside the RCTWebSocketExecutor.mm file to point to your local machine. Once done, remote JavaScript debugging can be triggered via the Developer Menu.
Once your environment is configured, several tools can help you gain deeper insight into your app’s behavior.
Redux DevTools is a powerful tool for monitoring app state over time. It allows you to inspect each dispatched action, view the state before and after, and even time-travel through your app’s state history. When you're dealing with complex data flows or hard-to-reproduce bugs, Redux DevTools often makes the debugging process more manageable.
The React Profiler is another valuable utility. It helps you measure how often components render and how long each render takes. This is especially useful when trying to improve app performance or detect unnecessary re-renders. The profiler can be accessed via React Developer Tools and integrated into the development workflow without much overhead.
Flipper is a desktop app built specifically for debugging React Native and native apps. It provides a unified interface for viewing logs, inspecting network requests, monitoring performance, and debugging layouts. With plugins like React DevTools, AsyncStorage viewer, and native logs, Flipper becomes a single place to observe both the JavaScript and native aspects of your app.
While tools are essential, debugging also depends heavily on how code is written and maintained. Clear variable names and well-structured functions reduce the mental overhead when navigating code during a debugging session. Adding concise comments where logic is non-obvious can save time for both you and others working on the project.
It also helps to regularly test your code, not just manually but through automated tests. Writing unit and integration tests can eliminate many issues before they reach the debugging stage. In production workflows, continuous integration systems can automatically run test suites and build checks every time code is committed. This makes it easier to identify bugs early and maintain overall code stability.
Debugging React Native applications involves a combination of practical setup, smart tooling choices, and clean coding habits. The better you understand each of these areas, the faster you’ll be able to identify problems and ship stable apps.
We hope you find this article useful. In this article, we have discussed some React Native debugging tools and techniques that will help you debug your application and save you time.
At Brilworks, we offer React Native development services. Whether you need to build a new app, modernize an existing one, or fix bugs, our team is ready to help. If you're looking to hire React Native developer, connect with us today to get started.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements