COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








Artificial intelligence is a topic of widespread discussion today, with everyone from professionals to the general public talking about its potential impact on our lives and jobs. With so much conversation, we frequently encounter many terms such as machine learning, NLP, generative AI, prompt, large language models, etc.
In this Generative AI glossary, we’ve curated essential terms and definitions that frequently appear when we learn about AI. These are terms you'll likely encounter today or in the near future.
Whether you're a business owner or an enthusiast eager to learn about artificial intelligence, this glossary will help you better understand generative AI terminology and concepts.
AI has existed since the 1950s; however, many people were unaware of this transformative technology until the 2020s. It was not widespread until the launch of ChatGPT, which took the Internet by storm by reaching millions of users in just five days—a feat that took Instagram, Netflix, and Spotify months or years.
Now, several AI-powered tools are available for content marketers, designers, and business owners, taking productivity and creativity to the next level. With their growing popularity, netizens are also getting confused with new AI terminology.
Generative AI terms are popping up everywhere with the emergence of popular tools such as ChatGPT, Bard, and others. This landscape could be exciting and confusing for beginners, as several terms are used interchangeably.
Though the list is comprehensive with hundreds of words, we will be jotting down some of the most popular Gen AI terminologies that every professional should know.
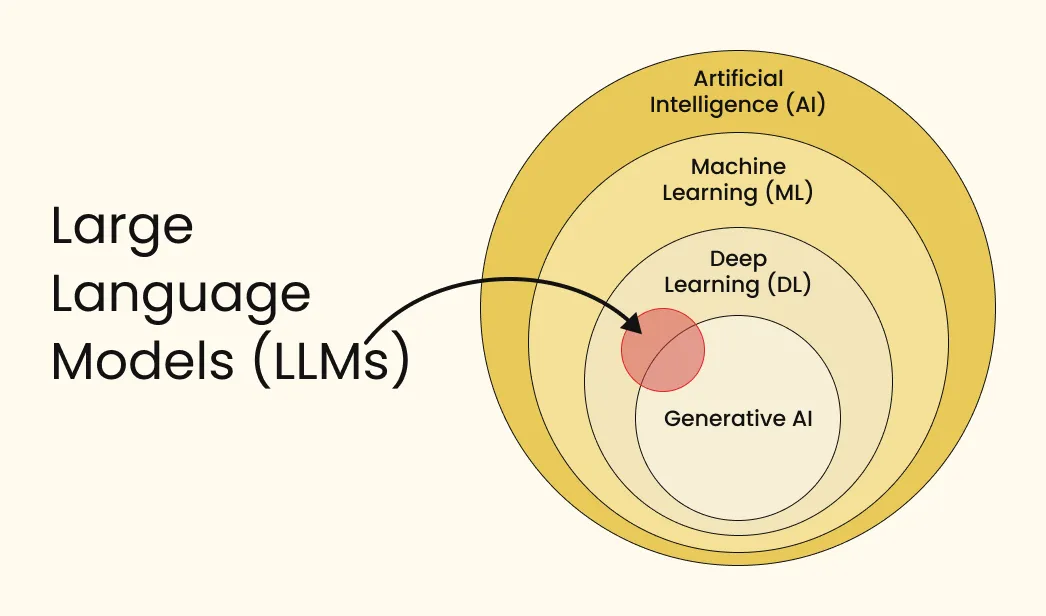
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad field focused on creating machines and programs to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. An AI-powered machine or program can perform tasks such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, understanding natural language, and perception.
AI was conceptualized in the 1940s and 1950s, with the aim of enabling machines to think and operate autonomously. Over the decades, AI has developed into various subsets, including generative AI, which can create text, images, music, and more.
If you want to explore AI platforms shaping the future, read our guide on Best Artificial Intelligence Platforms.
Neural networks are inspired by neurons that make decisions in a manner similar to the human brain. Neurons are cells in the brain that transmit data throughout the body. A neural network consists of interconnected nodes that process and learn from data.
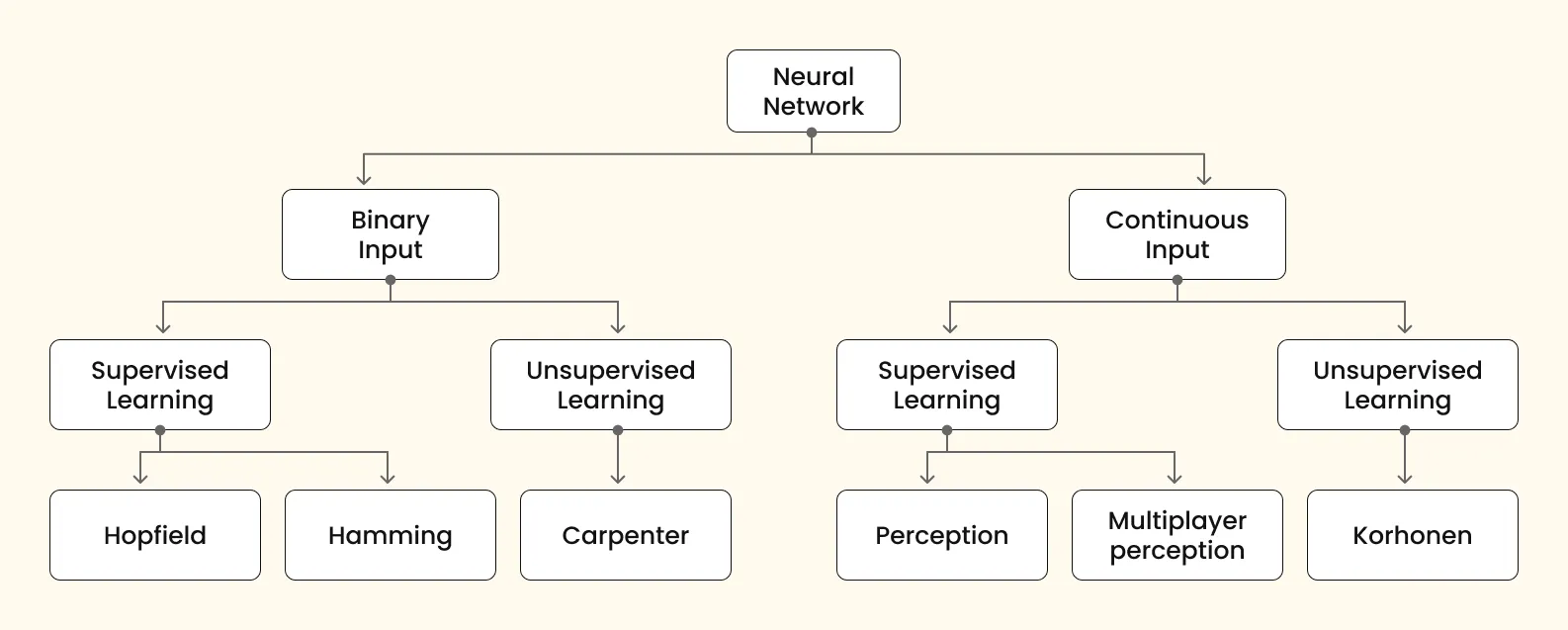
There are different types of artificial neural networks exist today:
GPT stands for generative pre-trained transformer. It is developed by OpenAI, the company behind the popular ChatGPT tool. ChatGPT contains GPT, so now you might be wondering exactly what a generative pre-trained transformer(GPT) is.
Apart from ChatGPT, millions of other generative AI models (or applications) surfacing across the Internet are built upon GPT. This means that GPT operates with some custom modifications behind the scenes.
Major chatbots write in similar tones because they, in the end, have the same brain or program (or GPT model). The model can be considered the brain of your program.
NLP stands for Natural Language Processing. It refers to processing natural languages like those we speak and write. Nowadays, machines are capable of understanding and processing our natural language. You can communicate with them using your everyday language, and they can grasp your intent.
NLP is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables interactions between machines and humans. When a system, machine, or program has NLP ability, you can interact with it using your own language.
For example, AI Chatbots can understand sentiments like humans and respond appropriately. Have you ever wondered how they do it? The NLP technology behind them powers them to understand our sentiments.
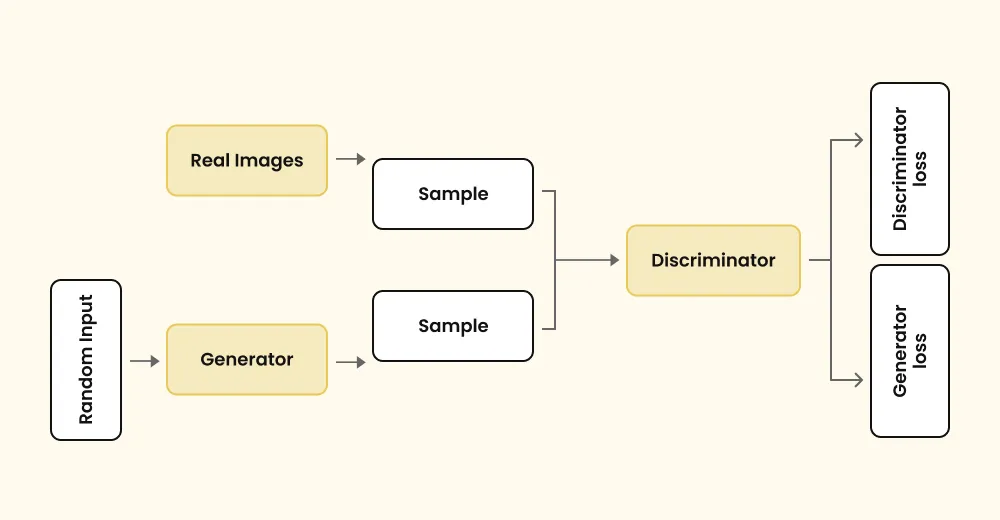
GAN stands for Generative Adversarial Network, a type of neural network model. In this model, two neural networks compete against each other to generate authentic results. One network generates new data, while the other tries to distinguish if it's real or fake. They continue improving until the second network can't determine fake from real anymore. GAN includes a generator and a discriminator, two neural networks that work in tandem to generate content.
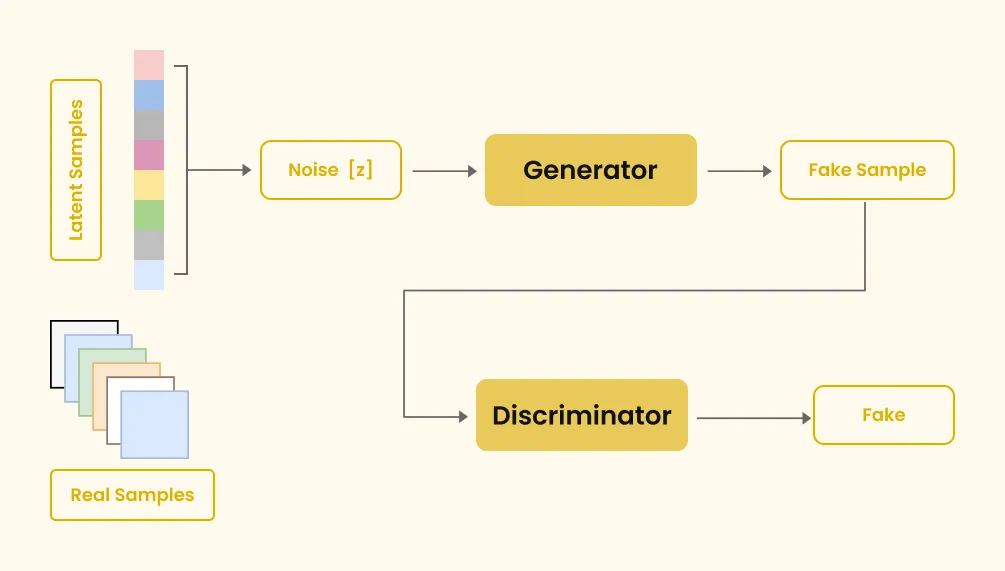
When someone criticizes something you create, it allows for improvement, and this iterative pattern is also applied in machine learning.
The discriminator is a type of neural network that competes against a generator in a GAN (Generative Adversarial Network) to help the generator produce data indistinguishable from real data. Artificial intelligence is indeed trained through a process similar to how humans learn.
LLM stands for large language models. In AI, a large language model refers to a computer program that is trained on massive amounts of text data from the Internet, books, articles, and more—thousands or millions of gigabytes' worth of text. Based on its learning, it can understand written language, write essays, answer questions, and even hold conversations.
Famous examples of large language models (LLMs):
For practical applications of these models beyond ChatGPT, see Beyond ChatGPT: Trending AI Tools.
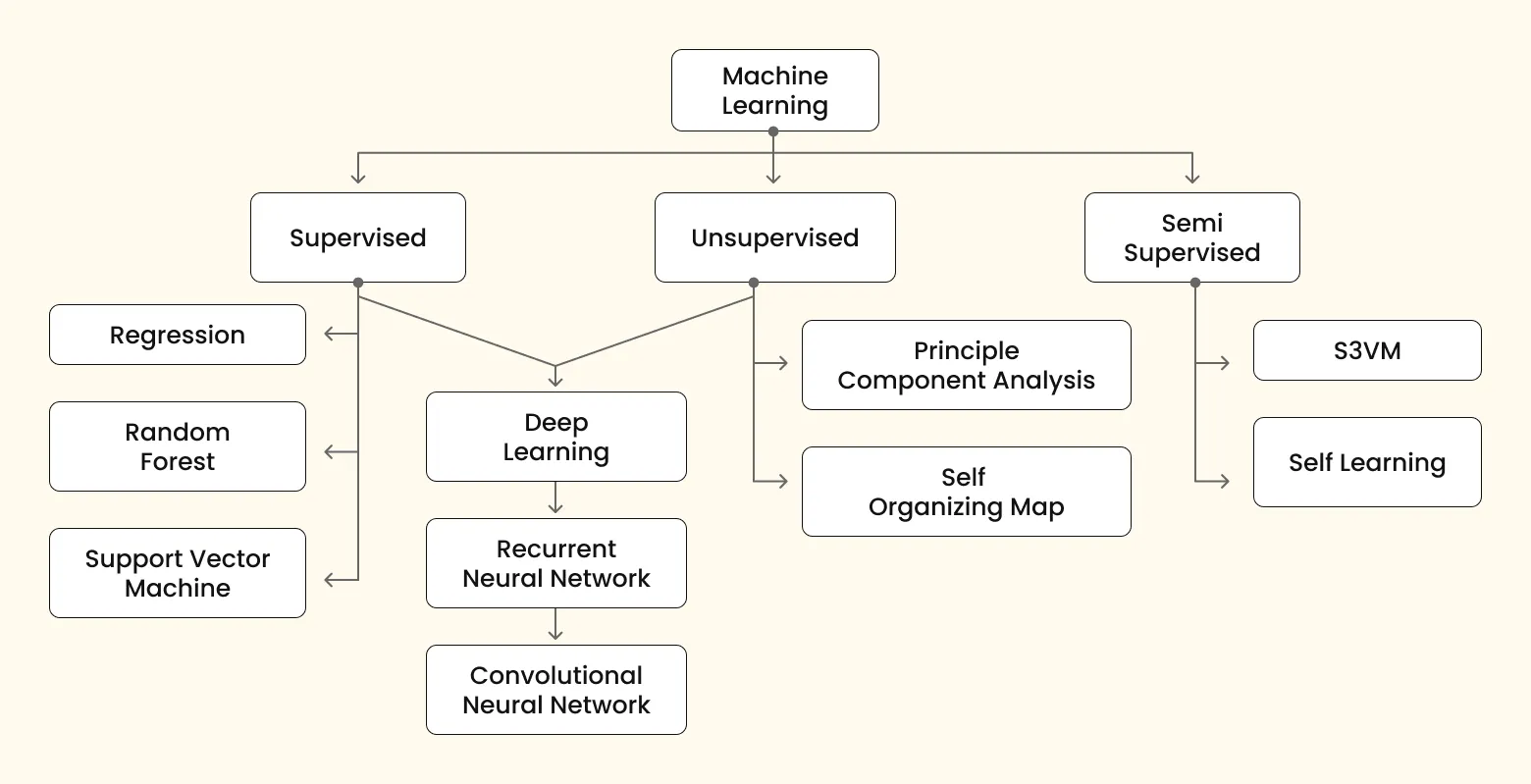
In the field of AI, different methods are used to train AI models. One prominent approach involves neural networks with many layers (hence "deep") to model complex patterns in data. Deep learning has revolutionized many fields within artificial int lligence. However, it's important to note that deep learning is just one approach among several in machine learning.
AI models, or artificial intelligence models, are computer programs that find patterns in large data sets. They can take in information, analyze it, and then make decisions based on what they learn. As we have learned, ChatGPT and Google's Gemini are AI models, specifically large models.
Several machine learning models utilize supervised learning, a subset of machine learning that uses labeled datasets to train algorithms to recognize patterns. Data labeling in machine learning is identifying and labeling raw data.
For example, a label may indicate if the object is a bird or a car. Labelers may assign tags by simply saying yes/no. In supervised learning, the ML model uses human-provided labels to learn the underlying patterns in a process called "model training."
In unsupervised learning, machines learn without human supervision. In this learning, the machine receives raw data to discern patterns and insights without explicit guidance or instruction.
Multi-model AI programs are gaining traction in 2025 as they develop advanced capabilities to process a variety of inputs, including text, images, audio, and video, and convert these inputs into different formats. Google's GEMINI is a popular multi-model AI program that can read and extract data from images.
Reinforcement learning (RL) is a type of machine learning in which software learns to make decisions through trial and error. It mimics how humans learn by trying different actions and remembering what works. Good actions are rewarded, and bad ones are ignored.
RL algorithms use rewards and punishments to learn the best way to achieve their goals. They can even handle situations where they need to make short-term sacrifices for long-term benefits. This makes RL a powerful tool for training AI to perform well in new and unpredictable situations.
A prompt in AI is a command written in natural human language that describes the task the AI model should perform. A prompt can be text, images, or any other data. The quality and specificity of the prompt can significantly influence the quality and relevance of the generated output.
In A, a token is a basic unit of data that algorithms process, especially in natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning. Tokens are part of a larger dataset and can be words, characters, or phrases.
For instance, when handling text, a sentence is split into tokens, where each word or punctuation mark is a separate token. This step, tokenization, is essential for preparing data for AI models.
Tokens are not limited to text. They can represent different data types, and are vital for AI to understand and learn from them. In computer vision, a token might be an image segment, like a group of pi els or a single pixel. In audio processing, a token could be a short snippet of sound. This versatility makes tokens crucial for AI to interpret and learn from various forms of data.
In AI, hallucinations refer to instances where a model generates an output that seems plausible but is incorrect or nonsensical. This is common in natural language processing (NLP) when an AI system produces text that looks coherent but is factually wrong or misleading.
For example, a chatbot might confidently provide a made-up answer to a question, or a text generation model might invent details that were not present in the original data. Hallucinations occur because the model predicts based on patterns it learned during training rather than verifying the accuracy of the information.
Generative mode s are a type of AI that creates new data similar to the data they were trained on. They learn the underlying patterns and structures of the training data and use this knowledge to produce new, similar instances. For example, a generative model trained on text data can make new sentences or paragraphs that mimic the style and content of the original text.
Similarly, in image processing, a generative model can create new images that resemble the training images. These models are widely used in applications like text generation and image synthesis.
Artificial intelligence is evolving rapidly, and Gen AI terminology is becoming part of everyday conversations. From GPTs and LLMs to prompts and GANs, these concepts form the foundation of modern AI development.
While many blogs cover 10 or 12 artificial intelligence terms, we’ve expanded this generative AI glossary to 17 of the most relevant concepts you must know in 2024.
If you’re exploring how to integrate these technologies into your business, check out our Generative AI Development Services or continue reading more about AI development on our blog.
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence or part of it. It is a branch of computer science that enables computers to learn from data and make decisions and predictions without any external help.
Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence possessed by machines, such as computers, mobile phones, smart robots, etc.
An AI algorithm is a set of instructions to be followed by a computer or machine in order to learn how to perform tasks and make decisions.
The most common AI terms include machine learning, neural networks, GPT, LLM, NLP, and prompts. These are the building blocks of generative AI.
General AI terms cover broader concepts like algorithms, supervised learning, and deep learning, while generative AI terminology focuses on models that create new outputs (e.g., GANs, LLMs, prompts).
Beginners should start with understanding AI, machine learning, neural networks, GPT, LLM, and NLP before diving deeper into advanced concepts like reinforcement learning or multi-modal AI.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements