COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES







Artificial intelligence isn't a monolith. As tools like ChatGPT overwhelm with human-like creativity, agentic AI is emerging. Both technologies are transforming businesses and professional workplaces and reshaping industries. They are different, and confusing them could be a critical mistake. One creates, and the other acts.
Generative AI burst into the public domain in 2022. It created poems, code, and synthetic media, mimicking human creativity. It's been more than three years, and now Agentic AI is stepping into the spotlight. It takes AI capabilities one step further, autonomously executing tasks and making decisions.
In short;
In this post, we'll learn the difference between the two. Learn why businesses that leverage the correct type of AI for the right task will dominate the next decade.
75% of enterprises now blend both AI types. If you’re unsure where to start, specialized generative AI development services can prototype the optimal mix for your workflow.
Generative AI is responsive; that is, when users make a prompt, it can respond in a personalized manner based not only on the prompt but also on previous user interactions and experience. For instance, if you instruct generative AI to write a blog post or create an image, it processes the prompt and generates an output based on patterns learned from its data.
Generative AI is remarkable, particularly for content generation, and is a valuable tool for human professionals to enhance their writing. The thing is, it needs guidance from humans for a lot of tasks (like visual design).
Agency AI is proactive. It can perform tasks or initiate actions without prompts. It can analyze the context, set goals, and perform multi-step tasks. For example, an AI agent can monitor the level of inventory and reorder products automatically.
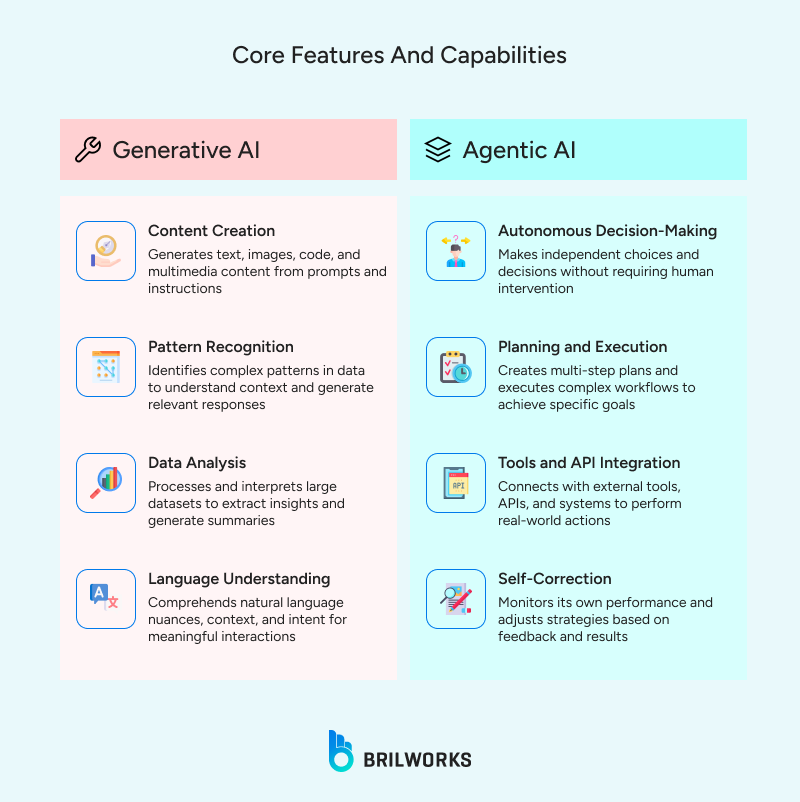
On the autonomy spectrum, generative AI occupies the reactive end. It is best suited to controlled, creative tasks but lacks initiative. It relies on human instructions. Agentic AI sits closer to full autonomy. It can independently make decisions and adapt to dynamic environments.
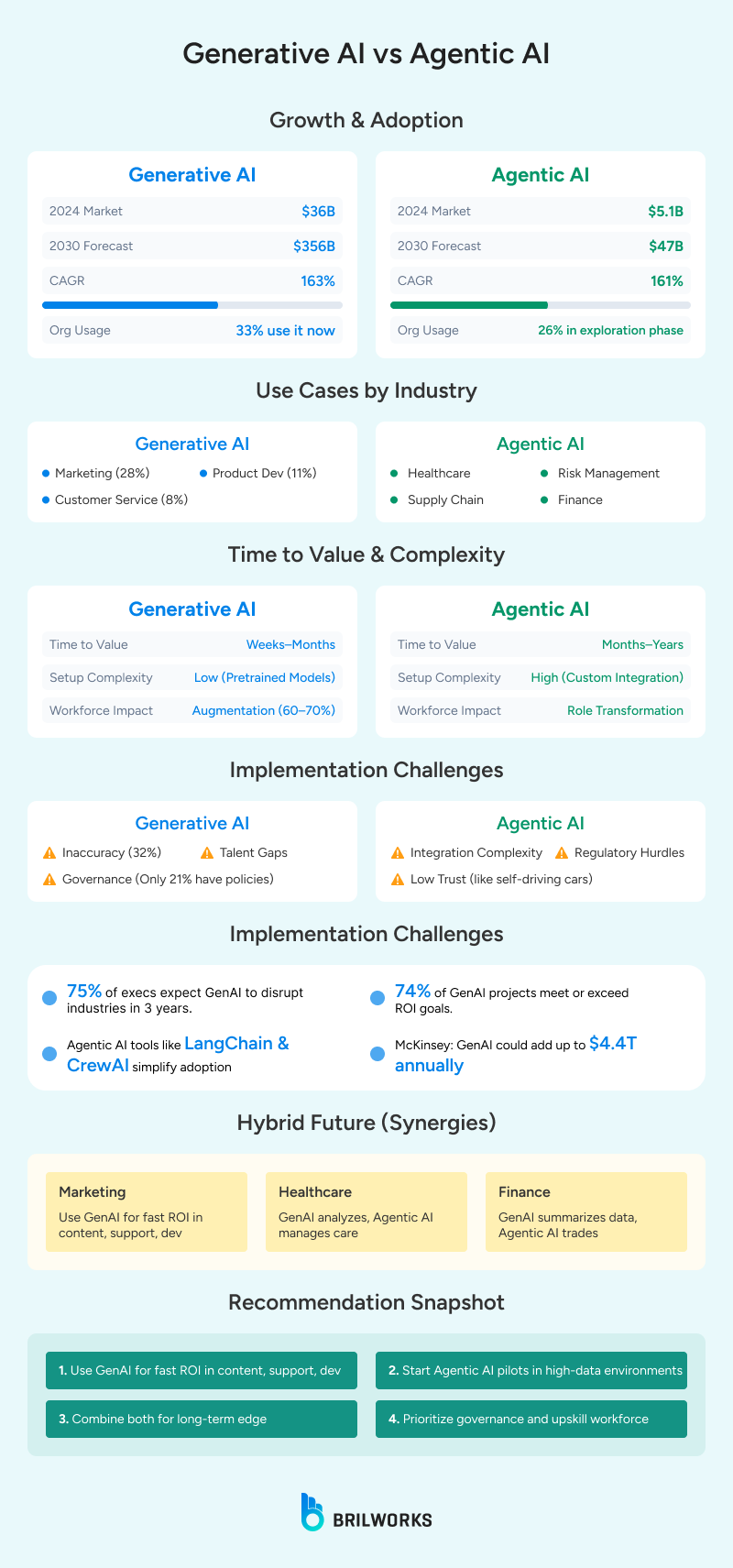
Generative AI is a remarkable technology for generating multiple content types. According to Deloitte's 2023 Creator Economy in 3D survey, 94% of brands working with content creators are currently using generative AI or planning to implement generative AI in the future. Of those brands, 55% are using generative AI in some capacity already. The other 39% of brands plan to use it in the forthcoming year.
Its capabilities are what make it the best AI approach for organizational needs, focusing on experiential and analytical tasks. Below are its main advantages, all of which have practical examples showing real-world value.
Generative AI generates text, images, and code, enabling professionals to focus on their critical tasks. Generative AI tools can suggest ideas, even write entire blog posts, website pages, research papers, and summarize documents. As a result, users can reduce a significant amount of time spent brainstorming and finding information. From blog pages to news articles, AI is changing the content creation industry like never before.
Tools equipped with LLMs can automatically generate social media posts and content calendars, and enhance content with emojis, images, and other visual elements.
Generative AI assists in content creation by identifying patterns. For example, it can write an entire article by predicting what may come next after a certain word. Traditional AI, also known as Narrow or Weak AI, is used to analyze data and make predictions based on the data. Siri and Alexa are popular examples of traditional AI, although these systems are being upgraded with generative AI. Generative AI systems, rather than relying on pattern recognition, execute pattern creation.
Service providers utilize generative AI to create personalized spaces for their users, as it can process vast amounts of information in a fraction of a second. Social media platforms exemplify data-driven thinking. Social media platforms display information based on the user's behaviors and preferences. For example, generative AI can utilize algorithms to recognize and create a highly personalized digital space.
It can be applied in different industries, such as e-commerce. An e-commerce owner can use this tech to analyze users' browsing history to create a personalized feed for them. Adobe reports that 4 out of 5 marketers see a positive return on investment (ROI) with personalized campaigns. Generative AI remarkably simplifies personalization efforts.
Generative AI technology can understand human languages. Therefore, advanced AI-powered chatbots are taking over customer service.
Tidio reports show that by 2025, AI will handle 95% of customer interactions.
Due to its exceptional skills in natural language processing, AI is altering the customer service industry. Besides, they can summarise meetings, acting as professional notetakers. Chatbot can now record your meetings,
ChatGPT can now record your meetings, making it easier for your team to skip manual notes and stay on top of follow-ups.
Generative AI can summarize an n-page market research report into a short brief in no time, which would have required many hours with a traditional approach.
Agentic AI is placed into business operations for autonomous tasks. It can work independently and plan and execute tasks with minimal human intervention. In 2025 alone, around 27% of enterprises are using agentic AI in production. Deloitte reports that the number will grow to 50% by 2027. The main reason behind rapid adoption by businesses is operational efficiency and cost reduction. Nearly 90% of adopters believe they will have a competitive edge with AI adoption.
Agentic AI evaluates situations and makes decisions without explicit human input. For example, a logistics company monitors traffic and weather data to suggest optimal rerouting of fleets.
Gartner and Boston Consulting Group report that logistics organizations reported a 25% improvement in operational efficiency with AI-driven decision-making.
Agentic AI divides complex tasks into actions and handles them step by step. Many industries, including manufacturing, will reap the benefits of agentic AI - this will improve demand forecasting, and resource allocation. Also, new multi-step workflow automation will allow for steps that would require much human coordination.
Agentic AI can be connected with systems, such as CRMs, databases, or third-party APIs, to perform tasks. In customer service, it integrates with ticketing systems to resolve issues.
Agentic AI learns from feedback and adjusts its strategies in real-time. This adaptability ensures continuous improvement, making it ideal for dynamic environments.
These abilities lead to significant business value through autonomous decision-making AI. For example, in cybersecurity, Agentic AI autonomously detects anomalies in network traffic and deploys the appropriate patches. In financial services, it autonomously executes trades based on market signals. In healthcare, it autonomously optimizes patient scheduling through integration with electronic health records.
Agentic AI and Generative AI offer distinct yet complementary capabilities. They are now critical tools for modern enterprises. By understanding agentic AI vs generative AI differences, businesses can select the best AI approach. Let's explore some practical applications.
Agentic AI is powerful for time-sensitive operations. It can detect anomalies in real-time. Therefore, businesses in financial services, cybersecurity, and supply chain management are big beneficiaries of agentic AI.
Generative AI transforms AI content creation and analytical tasks. Here are key applications with real-world examples:
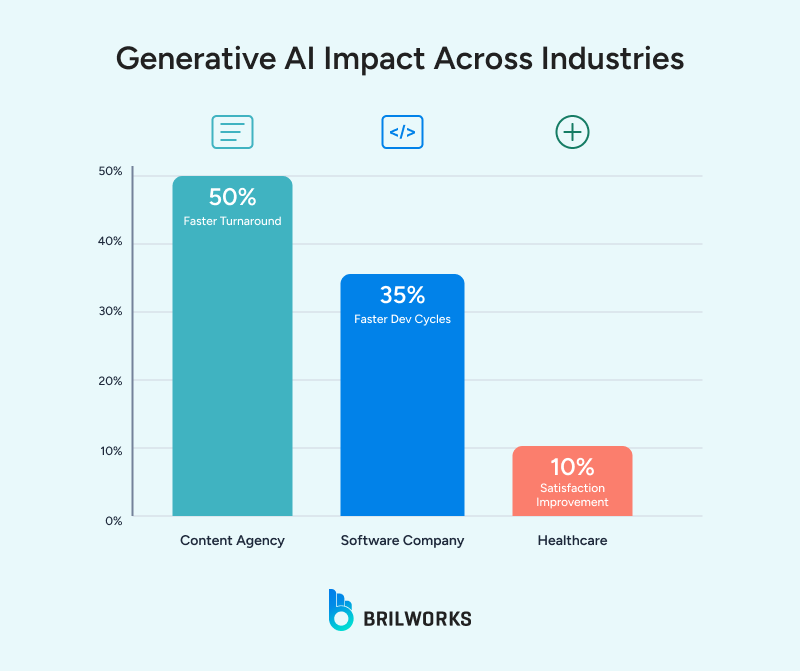
A 2025 Gartner study of 2,500 executives found that 38% prioritize Generative AI for customer experience, 26% for revenue growth, and 17% for cost optimization. This underscores Generative AI as the best AI approach for business creative needs, while Agentic AI supports operational efficiency, highlighting their complementary roles.
Generative AI has completely changed AI content creation and development. Marketing teams use it to produce blog posts, social media captions, and ad copy. Developers leverage it to generate code. Data analysts employ it to summarize datasets, uncovering trends in hours instead of days. It is now widely used in:
Hallucinations and context boundaries require human validation.
Leading companies leverage agentic AI vs generative AI differences for synergistic workflows. E-commerce platforms use Generative AI to create personalized spaces and agentic AI for dynamic pricing.

To select the best AI approach for business, evaluate agentic AI vs generative AI differences. Generative AI suits AI content creation tasks like marketing content, while Agentic AI excels in autonomous decision-making AI for automation, such as supply chain optimization. Ask: Are creative outputs or rapid decisions the priority? Pilot projects help test ROI before scaling.
Generative AI requires clean data and basic skills, while Agentic AI needs cloud infrastructure and API expertise. Key decision factors:
Generative AI faces GDPR compliance risks, while Agentic AI's autonomy raises accountability concerns. Both risk bias from skewed data. The EU AI Act governs high-risk systems, requiring strict oversight for autonomous decision-making AI. Human validation ensures accuracy in AI content creation.
Hallucinations (inaccurate outputs) plague Generative AI, and Agentic AI risks unintended actions. Mitigation strategies:
Artificial intelligence is evolving rapidly but not uniformly. Generative AI development has transformed business operations. It's the creative engine behind modern development and customer engagement.
Meanwhile, Agentic AI is focused on autonomy, task execution, and decision-making. It's reshaping operations, logistics, and planning across industries. Understanding the core differences, creation vs. action, reactivity vs. autonomy, is critical.
Businesses that align the right AI type with the right problem will lead the next wave of digital transformation. Use Generative AI to build ideas. Use Agentic AI to achieve outcomes.
Agentic AI focuses on autonomous decision-making and action, while generative AI specializes in creating content like text, images, and code based on patterns learned from training data. The former acts independently, while the latter typically responds to specific human prompts.
Evaluate your primary business needs—choose generative AI for content creation and data analysis tasks, and agentic AI for autonomous decision-making and time-sensitive operations that require minimal human intervention. Many businesses benefit from implementing both types for different use cases.
Agentic AI typically requires robust cloud infrastructure, API integration capabilities, and systems that allow for secure autonomous operations. You'll need data pipelines, monitoring tools, and governance frameworks that can support and oversee AI-driven decision-making processes.
Enterprise AI adoption is accelerating, with approximately 33% of enterprise software applications projected to include agentic capabilities by 2028, while generative AI continues to mature with improved accuracy and specialized industry applications. Organizations are increasingly implementing hybrid approaches that leverage both technologies. Remember to maintain a technical but accessible tone throughout, define all specialized terminology, and ensure the article provides clear, actionable guidance for businesses evaluating AI solutions.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements