COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








Fintech apps face high demands. They need to handle large volumes of sensitive data, process financial transactions reliably, and stay online under pressure. That is why Java fintech projects continue to be a top choice. Fintech Java solutions provide stability, security, and cross-platform consistency, which makes managing complex financial workflows much easier.
Banks, payment providers, and financial services still rely on Java to power account management, fraud detection, and other core operations. Its ecosystem of libraries and frameworks allows teams to speed up development while following Java security best practices.
This blog will explain why Java remains essential for modern fintech development, why companies trust it for financial platforms, and how it compares to other tech stacks.
The financial world is moving fast. Software has become the primary interface between users and their money, driving rapid growth in fintech.
The global fintech market is projected to grow from about $210 billion in 2024 to between $1.1 trillion and $1.5 trillion by 2033–a more than fivefold increase in less than a decade. This rapid growth makes choosing the right technology more critical than ever for fintech organizations looking to compete and scale successfully.
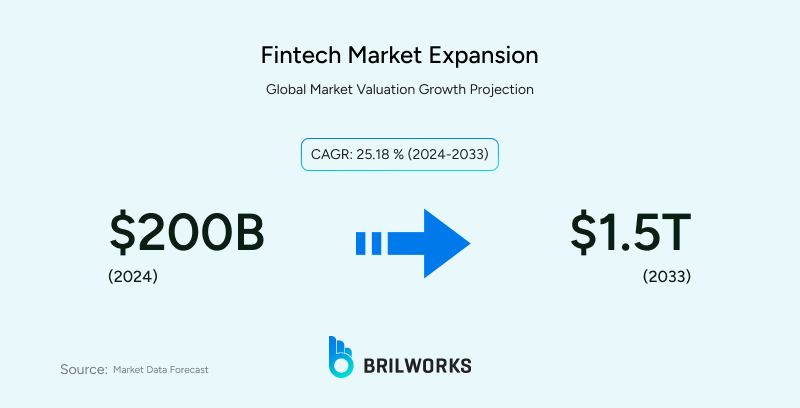
Along with performance, companies need to manage development cost in fintech, which depends on features, security requirements, and backend complexity.
Digital payments are among the fastest-growing fintech segments. As usage increases, platforms must handle more transactions and traffic while integrating trends like embedded finance, decentralized finance, and AI-powered financial tools.
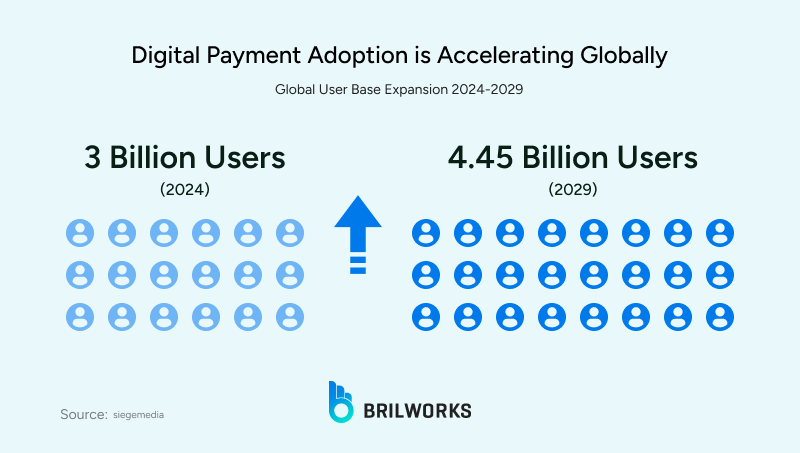
Using robust backend technologies like Java ensures reliability even as demands grow.
Java has been powering financial systems for decades. Its design for large-scale backend processes makes it ideal for fintech, where stability, security, and continuous performance are crucial. Key reasons Java continues to dominate include:

High transaction volumes, trading spikes, and payment surges require reliable performance. Java’s multithreading and memory management allow systems to handle simultaneous operations without freezing, powering high-frequency trading systems and core banking platforms.
See Also: Java Performance Tools and Best Practices Every Developer Should Know
Java is a reliable programming language for fintech security. It offers encryption, role-based access control, and secure communication from the start. Built-in tools like Java Security Manager reduce the need to rely heavily on third-party libraries.
Cross platform development saves time and reduces errors. Java applications run the same on servers, desktops, and mobile devices, supporting hybrid and cloud-native setups that are critical for fintech platforms.
Java allows incremental updates without breaking existing modules, which enables fintech teams to modernize gradually, as outlined in our Java modernization and migration blog.
Fintech apps can grow quickly. Java scales both vertically and horizontally, fitting monolithic architectures or microservices, so performance remains consistent even as usage increases.
Libraries and frameworks for payment processing, identity verification, and fraud detection simplify development. Tools like Spring Boot make managing large fintech codebases more efficient.
Java’s predictable support cycles from Oracle, Amazon, and Red Hat reduce maintenance risks and help ensure compliance over time.
Finding skilled Java developers is easier than with newer languages, making it simpler to hire Java developers or outsource fintech projects while maintaining speed and reliability.
The right framework improves development speed, maintainability, and security:
Spring Boot: Ideal for microservices, rapid development, and secure APIs.
Micronaut: Lightweight, optimized for cloud-native fintech apps.
Quarkus: Fast startup and low memory footprint, suited for real-time platforms.
Jakarta EE: Mature and stable, best for large enterprise systems.
Framework selection depends on project scale, architecture, and compliance requirements. Learn more in our top Java frameworks blog.
Security is critical in fintech. Enterprise Java provides a predictable and well-tested security model, enhanced when developers follow best practices in Java development.
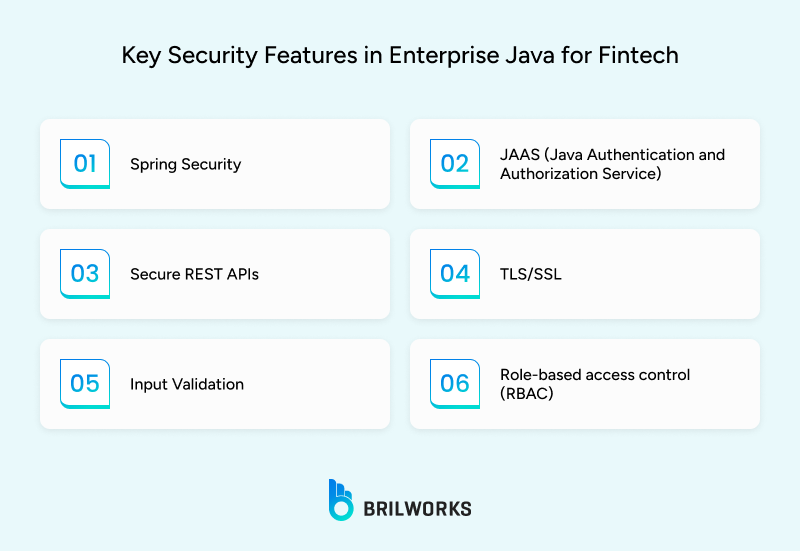
Key features include:
Spring Security: Handles authentication, sessions, and layered protection.
JAAS: Manages roles and access to sensitive parts of the system.
Secure REST APIs: Uses token-based authentication, input sanitization, and encrypted transfers.
TLS/SSL: Native support for encrypted communication.
Input Validation: Prevents injection attacks and ensures data integrity.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Restricts access based on user roles.
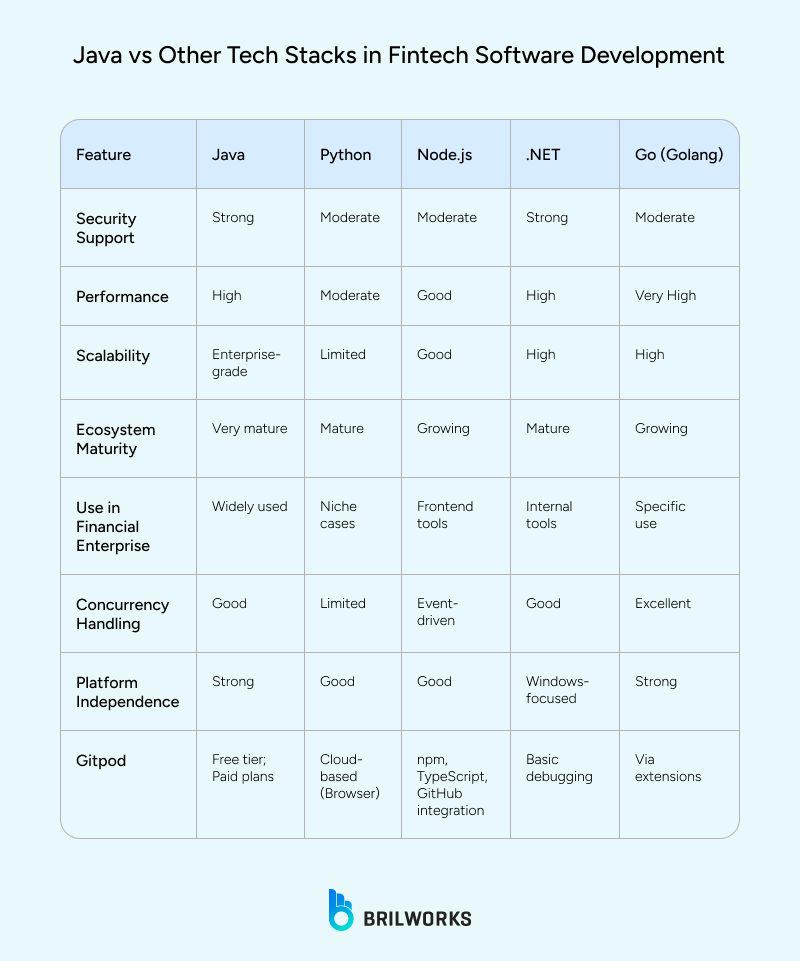
While other stacks have advantages, Java remains the most reliable:
Python: Great for prototyping, analytics, and machine learning, but less suitable for high-volume transactions. See Java vs Python.
Node.js: Fast and event-driven, but requires extra attention for secure fintech systems.
.NET: Strong security and enterprise support, but less cross-platform flexibility.
Go (Golang): Fast and concurrent, suitable for microservices, but with a smaller ecosystem. See Java vs Go.
Java powers high-performance fintech platforms:
PayPal: Uses fintech digital payment systems with Java, managing millions of transactions per second.
Goldman Sachs: Supports trading and risk management tools.
Revolut: Manages accounts, transactions, and compliance operations.
Java also extends to AI and machine learning, enabling data-intensive, high-performance workloads. Learn more in Java’s growing involvement in AI and machine learning.
Java continues to be the backbone of fintech app development due to its stability, security, scalability, and mature ecosystem. Financial institutions rely on it for managing sensitive data and daily operations.
Keeping up with modern frameworks and best practices ensures fintech projects remain secure and maintainable. The right team is equally important, so make sure to hire Java developers with experience in financial systems and compliance.
For fintech teams seeking a reliable backend, Java remains a proven, future-proof choice.
Java offers strong security, scalability, and long-term support, which makes it a reliable choice for fintech applications where performance and stability are essential.
Java has built-in security features like access control, cryptography APIs, and memory management that help reduce vulnerabilities in financial systems.
Java is often chosen for large-scale and complex financial systems, while Python is favored for analytics and Node.js for lightweight services. Each has its role depending on the use case.
PayPal and other major platforms rely on Java for handling millions of transactions daily thanks to its performance and security benefits.
Yes, hiring Java developers is a smart choice for fintech startups aiming to build secure, scalable apps with enterprise-grade performance.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements