COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








Project Loom: Virtual threads make concurrency simpler and more intuitive
Cloud-Native Development: Container-ready apps with automatic scaling
Serverless Java: Practical performance for cloud functions
DevOps Integration: Automated, secure release processes
Spring Framework Updates: Cloud-ready, reactive, and GraalVM compatible
Reactive Programming: Efficient non-blocking applications
AI and Machine Learning: Production-ready enterprise AI tools
Git and Code Collaboration: Streamlined workflows for distributed teams
Remote Development Tools: Cloud IDEs and secure access solutions
Mobile and Android Development: Backend and API support
Java has been a steady player in software development for over 25 years, and it continues to evolve. With Java 25 on the horizon and enterprises embracing modern architectures, developers need to keep pace with the latest trends.
Each release brings improvements that make Java more efficient, flexible, and cloud-ready, as outlined in each new version. The rise of cloud-native development, serverless computing, and AI is shaping frameworks like Spring and other Java frameworks in enterprise development.
Whether you are managing large enterprise systems, building cloud applications, or supporting mobile projects, understanding these ten trends is essential for staying competitive.
Project Loom brings virtual threads to Java, making concurrent programming much simpler. Developers can write code that feels synchronous while handling thousands of tasks efficiently.
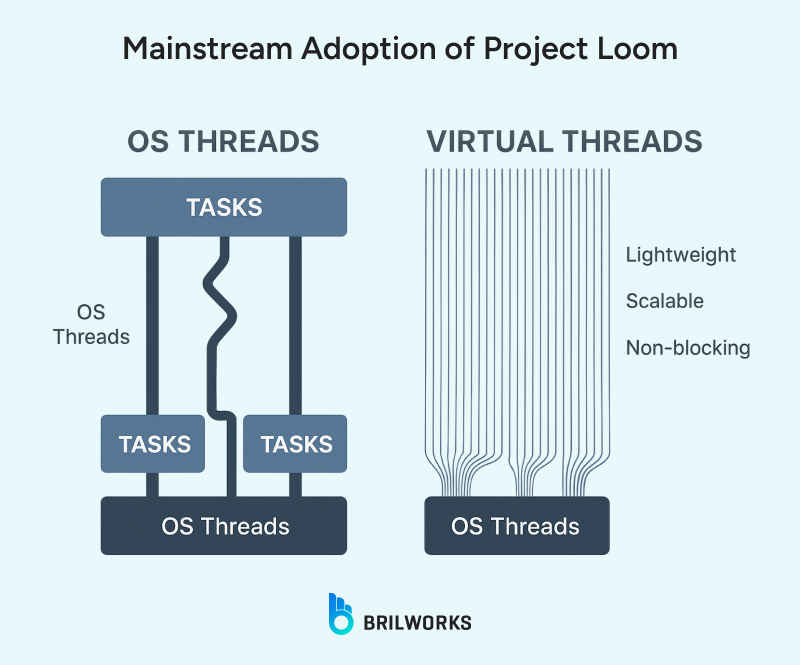
Frameworks are increasingly supporting virtual threads in production environments, which makes Loom an important consideration for enterprise development. This approach reduces context-switching overhead while keeping the code clear and maintainable.
Building Java applications for the cloud is no longer optional. Modern systems rely on containerization, distributed services, and microservices architecture. Java integrates seamlessly with platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, and leverages managed services like databases and messaging systems.
Applications can scale automatically, and patterns like retry logic, circuit breakers, and health checks ensure resilience. Teams developing Java cloud applications can focus on features rather than infrastructure.
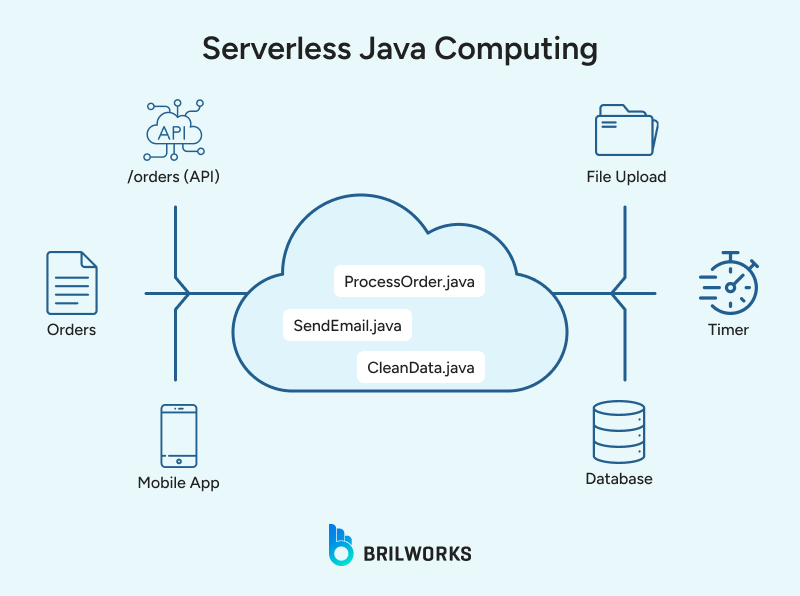
Serverless computing has finally become practical for Java developers. Improvements like GraalVM native images and optimized JVM startup times allow Java functions to start quickly even in cold-start scenarios.
Frameworks such as Spring Cloud Function, Micronaut, and Quarkus simplify serverless development, letting teams stay within the Java ecosystem while reducing cloud costs and supporting event-driven architectures.

DevOps has reshaped how Java applications are delivered. Instead of long release cycles, teams now deploy smaller, automated, and secure updates more frequently.
CI/CD pipelines, automated builds, and compliance checks allow teams to deploy code confidently across multiple environments, maintaining stability while delivering features faster.
Spring Boot continues to be the framework of choice for enterprise applications. The 2025 updates, including Spring Framework 7 and Spring Boot 4, improve cloud compatibility, observability, and native image support.
Reactive programming and virtual thread support make Spring suitable for building microservices and scalable enterprise projects. Developers skilled in Spring are in high demand, making hire Java developers a strategic move for teams.
Reactive programming is now a standard approach for performance-critical applications. Unlike traditional models, it avoids blocking threads and can handle many tasks simultaneously.
Libraries like Project Reactor, RxJava, and Spring WebFlux support Java frameworks in production, helping developers build responsive, scalable cloud and microservices applications.

Java is well-suited for production AI workloads, handling large volumes of data while ensuring security and scalability. Libraries like Deeplearning4j, TensorFlow Java, Weka, Spark MLlib, and newer tools such as Spring AI and Langchain4j make AI integration smoother.
AI is also changing how developers work, with tools providing code suggestions and automated testing. Learn more about Java in AI/ML.
Git remains the go-to version control system for Java teams. It integrates with IDEs like IntelliJ and Eclipse, build tools like Maven and Gradle, and CI/CD pipelines, supporting distributed workflows efficiently.
Features like signed commits, audit logs, and secret scanning ensure secure and compliant development processes, making Git essential for enterprise development.

Remote and hybrid work has made secure remote access a necessity. Cloud IDEs like GitHub Codespaces and Eclipse Theia, along with VPN alternatives and containerized environments, allow developers to code from anywhere. Remote tools maintain productivity and consistency without compromising security.

Java remains relevant in Android and mobile backend development. While Kotlin has grown in popularity, Java continues to power core libraries, APIs, and backend services for mobile apps. Teams rely on Java for stable, maintainable solutions, making expertise in Java APIs critical.
Java continues to evolve to meet modern development needs. Its role in cloud-native systems, microservices, AI, and mobile backends keeps it relevant.
Teams managing complex software or large codebases benefit from hiring Java developers who understand these trends, ensuring projects remain scalable, maintainable, and future-ready.
Project Loom, cloud-native development, serverless Java, AI integration, reactive programming, and Spring updates.
Loom is gaining mainstream adoption, with frameworks increasingly supporting virtual threads in production.
Spring Boot, Micronaut, Quarkus, and frameworks supporting reactive programming.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements