COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








Mobile app development frameworks are software tools that help developers create applications for different devices and operating systems using the same code base. This lets developers build apps for iOS and Android without writing separate code for each. It is a common approach in cross platform mobile app development because it saves time and reduces repeated work.
These frameworks are built on different app development technologies. Some work with web based tools like HTML, CSS and JavaScript. Others use programming languages such as Dart, Kotlin, Swift, Java, or Python. Each framework has its own way of structuring an app and managing how it runs on different devices.
Some frameworks are better for apps that need strong performance and full access to device features. Others are more suited for projects that require quick development and regular updates. The choice depends on the type of app you are building, the skills of your team, the budget and how you plan to maintain the app in the future.
This blog explores the most popular mobile app development frameworks of 2025. It includes options for different project needs and a simple framework comparison so you can understand their main features before reading about each one in detail.
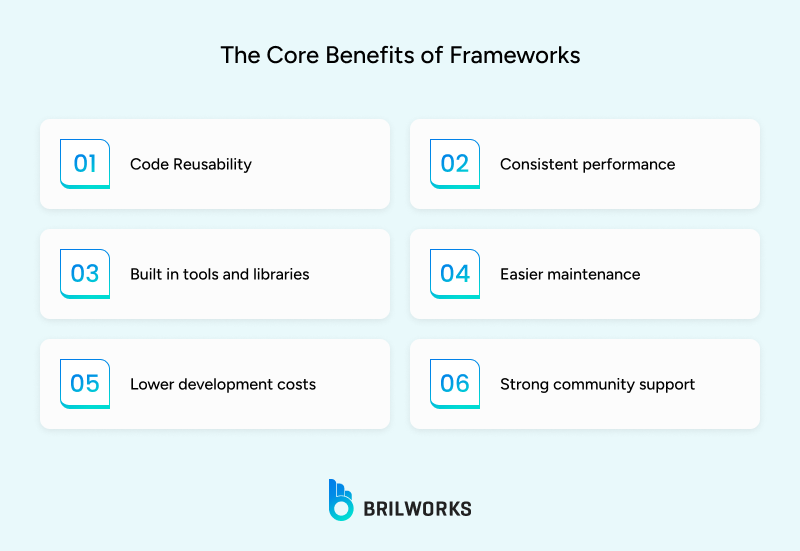
Mobile app development frameworks help developers create apps faster and with less repeated work. They make it possible to use the same set of code for different platforms which helps keep projects easier to manage. These benefits matter for small projects and for larger systems as well.
A major benefit is the ability to use the same code across multiple platforms. This is common in cross platform development, where most of the app’s logic works for both iOS and Android. Developers can put their focus on building features instead of writing the same function for different systems. This makes code reviews simpler and keeps the structure easier to follow over time.
Frameworks give access to native device features in a single process, which helps the app behave in a steady way on different operating systems. Tasks like using the camera, GPS, or storage work in the same process for all versions of the app. This lowers the chance of bugs that appear when different sets of code respond in separate ways.
Many frameworks come with ready-made libraries, templates, and testing tools. These save time by giving developers a base to start from instead of building every component from the ground up. It allows more attention to be placed on the parts of the app that are unique, rather than spending time on basic elements.
A single code base makes updates and fixes quicker to manage. When a change is made, it can be applied to every platform without needing separate updates. This avoids cases where one version of the app works differently because it has missed a change. It also makes the release process smoother.
Since most of the code works for more than one platform, less development time is needed. This can make the process more cost effective compared to creating separate apps for each platform. It is a practical approach when the budget or timeline is limited.
Popular frameworks often have active developer communities that share plugins, code samples, and solutions to common problems. This makes it easier to solve technical issues without long delays. A healthy community also means the framework is more likely to stay updated for the future.
Now let’s take a look at some of the best frameworks in mobile app development.

React Native is an open source framework created by Meta. It is one of the preferred frameworks for building cross-platform apps. React native app development is designed to help developers build mobile apps for iOS and Android using JavaScript and React. The goal is to write most of the code once and run it on both platforms, which can reduce development time and effort.
The framework connects JavaScript code to native components so the apps feel close to native in performance and design. Developers can use pre-built components for common functions or integrate native modules when they need access to specific device features like the camera or push notifications.
Bloomberg
Walmart
Works on both iOS and Android with a shared code base
Large community and active support
Live reload speeds up testing and development
Access to native device features through modules
Rich library of pre-built components
Some performance limits compared to fully native apps
May require native development skills for advanced features
UI may need extra adjustments for different platforms
For teams deciding between these two popular options, understanding the differences between React Native and Ionic can help clarify which one fits your project better.
Ionic is a free, open-source framework that leverages standard web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create mobile apps. It is built on top of Angular by default, but also supports React and Vue. This flexibility makes it easier for developers who already know these web frameworks to start building mobile apps without learning entirely new languages, especially if they’re already familiar with popular JavaScript frameworks for app development.
Apps built with Ionic run inside a WebVie,w which displays the app interface. The framework offers a large set of UI components that are styled to look and feel like native elements. Developers can also connect to device features using plugins provided by the Capacitor or Cordova platforms.
MarketWatch
Pacifica
Sworkit
Diesel
Uses familiar web development skills
Works with Angular, React, and Vue
Large library of ready-to-use UI components
Cross-platform development with a single code base
Good plugin support for accessing device features
Performance may not match fully native apps for heavy graphics or animations
Reliance on WebView can cause minor rendering delays
Some plugins may need extra configuration for different platforms
Flutter is an open-source UI framework created by Google that enables the development of mobile, web, and desktop applications using a single codebase. It uses the Dart programming language and focuses on delivering fast performance with a consistent UI across platforms.
Instead of relying on native UI components, Flutter uses its own rendering engine to draw widgets directly on the screen. This approach allows developers to create highly customizable designs and maintain consistent behavior across devices. It also includes a wide range of built-in widgets for layout, navigation, and animation.
Google Ads
Alibaba
Reflectly
BMW
Single code base for multiple platforms
High performance through a custom rendering engine
Large collection of pre-built and customizable widgets
Hot reload speeds up development
Strong community and growing ecosystem
Larger app size compared to some frameworks
Requires learning the Dart language
Limited availability of some third-party libraries compared to older frameworks
Angular mobile app development uses the Angular framework, which is a TypeScript-based tool created by Google. While Angular is mostly known for building web applications, it can also be adapted for mobile projects through platforms like Ionic or NativeScript. Developers who already work with Angular for web projects can carry over much of their knowledge to mobile development.
When paired with a mobile-focused framework, Angular mobile app development offers structure and tools that support building scalable applications. Features like dependency injection, two-way data binding, and modular architecture help manage complex app logic while keeping the code organized. Read our full comparison between React Native vs Angular.
Gmail
Microsoft Office Online (mobile web)
Upwork (mobile site and hybrid apps)
Mixer
Strong structure for managing complex applications
Reusable code across web and mobile projects
Backed by Google with regular updates
Works well with frameworks like Ionic and NativeScript
Strong TypeScript support improves maintainability
Steeper learning curve for beginners
Performance can depend on the mobile framework used alongside it
Heavier initial bundle size compared to some lightweight frameworks
Xamarin app development is a framework from Microsoft that allows developers to create mobile applications for iOS and Android using C#. It uses the .NET platform, which means developers can share a large portion of code across platforms while still accessing native APIs.
Xamarin app development is often chosen by teams who already work in the Microsoft ecosystem. It integrates with Visual Studio, supports a strong set of libraries, and provides tools to build native like apps without writing separate code for each platform.
Alaska Airlines
The World Bank
Insightly CRM
Storyo
High code sharing between platforms
Strong integration with Microsoft tools
Provides access to native APIs with performance that closely matches native applications
Mature framework with active community
Larger app sizes compared to fully native solutions
Some platform-specific customizations may require extra work
Learning curve for developers new to C# or .NET
SwiftUI app development is focused on building iOS, iPadOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS applications using the Swift programming language. It is a user interface toolkit created by Apple that allows developers to design apps with a declarative syntax. This means the UI code describes what the interface should look like, and SwiftUI takes care of rendering it.
SwiftUI app development is tightly integrated with Xcode and Apple’s developer tools. It supports features like live previews, cross platform UI code sharing within Apple’s ecosystem, and smooth integration with Combine for managing data flow.
Apple’s own sample apps
Planny
Glimpse
BetterRest
Declarative syntax makes UI code cleaner
Tight integration with Apple’s platforms
Live previews speed up development
Supports accessibility and localization out of the box
Works only within Apple’s ecosystem
Some advanced features require fallback to UIKit
Limited backward compatibility for older OS versions
If you’re choosing between Apple’s native approach and a cross-platform option, exploring the React Native vs Swift key differences can provide valuable insight.
Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile app development is a framework from JetBrains that allows developers to share code between Android and iOS applications. It uses Kotlin as the primary programming language and supports writing shared logic for networking, data storage, and business rules while still creating platform-specific user interfaces.
Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile app development is often chosen by teams that want to reduce duplication without fully committing to a single UI framework. It allows full access to native APIs on both platforms, which means developers can keep the performance and look of a native app while still reusing most of the underlying code.
VMware
Philips Hue
Netflix (internal projects)
Careem
High code reuse for business logic
Full access to native APIs
Works well with existing native projects
Backed by JetBrains and supported by Google
UI code is not shared between platforms
Smaller community compared to older frameworks
Requires knowledge of native development for both iOS and Android
Similarly, weighing the pros and cons in a React Native vs Kotlin Multiplatform comparison can help teams decide on the right balance between code reuse and native UI flexibility.
NativeScript app development is an open-source framework for building mobile apps for iOS and Android using JavaScript or TypeScript. It allows developers to access native APIs directly from JavaScript without using wrappers, which makes it possible to build native like apps with a single codebase.
NativeScript app development supports integration with popular front-end frameworks like Angular and Vue. This flexibility makes it appealing for teams who already use these technologies for web development and want to extend them into mobile apps.
Strudel
Daily Nanny
Navadra
Sworkit
Direct access to native APIs
Support for multiple JavaScript frameworks
Single codebase for iOS and Android
Active open source community
Results in a larger application size compared to certain other frameworks.
Performance can be lower than fully native apps for complex features
Fewer pre built components compared to older frameworks
|
Framework |
Primary Language(s) |
Platforms Supported |
Code Reuse |
Access to Native APIs |
|
React Native |
JavaScript, TypeScript |
iOS, Android |
High |
Yes |
|
Ionic |
JavaScript, TypeScript |
iOS, Android, Web |
High |
Through plugins |
|
Flutter |
Dart |
iOS, Android, Web, Desktop |
High |
Yes |
|
Angular Mobile App Development |
JavaScript, TypeScript |
iOS, Android, Web |
High |
Through NativeScript/Cordova |
|
Xamarin |
C# |
iOS, Android, Windows |
High |
Yes |
|
SwiftUI |
Swift |
iOS, iPadOS, macOS, watchOS, tvOS |
Low (Apple ecosystem only) |
Yes |
|
Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile |
Kotlin |
iOS, Android |
Medium |
Yes |
|
NativeScript |
JavaScript, TypeScript |
iOS, Android |
High |
Yes |
|
jQuery Mobile |
JavaScript |
iOS, Android, Web |
High |
Through plugins |
|
Corona SDK (Solar2D) |
Lua |
iOS, Android, Windows, macOS |
High |
Yes |

Choosing a mobile app development framework depends on your project goals, the skills of your team, and the audience you want to reach. The decision affects how long development will take, the budget you will need, and how the app will perform once it is released. Focusing on a few key factors will make the choice simpler.
Decide which platforms your app will support. If you want to run on both iOS and Android, cross platform frameworks such as React Native, Flutter, Ionic, or Angular mobile app development can help you reuse code across platforms. If you are building for one platform, native options like SwiftUI for iOS or Kotlin for Android might be more suitable, especially for apps that demand strong performance.
Pick a framework that matches the programming languages and tools your team already knows. Developers with JavaScript experience may work better with React Native, Ionic, Angular mobile app development, or NativeScript. A team used to Swift may prefer SwiftUI. Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile fits well for teams already familiar with Kotlin, while teams working on server-side components might explore leading Java frameworks for backend and web projects. Choosing a familiar framework avoids delays from learning new technology.
Some frameworks let you create and maintain a single codebase for multiple platforms, which can save time and money. This can be useful for smaller budgets or short timelines. Native frameworks may cost more but can offer better performance and deeper access to platform features.
See Also: The Hidden Costs of Outsourcing Mobile App Development [How to Reduce Them]
Frameworks backed by a strong community are generally easier to work with. Large communities mean more guides, libraries, and solutions to common problems. Flutter and React Native are examples of frameworks that enjoy broad support. Smaller communities can make problem solving slower.
Before choosing a framework, try building a small version of your app with its main features. This will show how it performs, how easy it is to use, and whether it fits your needs. Testing on a small scale can prevent bigger issues later.
The right mobile app development framework can make building and maintaining your app easier. The choice depends on your project scope, available skills, budget, and how you plan to support the app after launch. Every framework has strengths and trade offs, so there is no single option that fits all needs.
If you understand your priorities and test your ideas early, you can choose a framework that works well for your team and your users. This approach helps you avoid costly changes later and gives you a clearer path from concept to release.
If you are planning your next mobile app development project, explore the frameworks we discussed and pick the one that aligns with your needs. Starting with the right tools can save time and effort throughout the development process.
There is no single best framework. It depends on your project goals, team skills, and target platforms. React Native, Flutter, and Ionic are popular choices for cross platform development. Native tools like SwiftUI or Kotlin suit single platform apps.
Both have strengths. React Native has a larger community and more third party libraries. Flutter offers faster performance and a consistent UI. Startups should choose based on their team’s skills and project needs.
Yes, Angular can be used for mobile apps when combined with frameworks like Ionic or NativeScript. It allows developers to build cross platform apps using web technologies and Angular tools.
Ionic apps use web technologies and run inside a WebView, which can affect performance. Native apps are built with platform specific languages and have direct access to device features, often resulting in better performance.
Native frameworks like SwiftUI and Kotlin generally offer the best performance. Among cross platform options, Flutter is known for fast and smooth performance due to its rendering engine.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements