COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








Two decades ago, mobile apps were built exclusively with native languages. Android relied on Java, while iOS applications were written in Swift. Cross-platform development frameworks existed but were nowhere near as dominant as they are today.
That changed when React Native entered the scene. Developed by a team at Meta (formerly Facebook), it redefined cross-platform development frameworks and changed how companies approach mobile app development.
This article explores React Native vs Native development, comparing both approaches head-to-head. We will outline their pros, cons, costs, and performance trade-offs, so by the end you’ll know which path suits your project best.
Leverage the expertise of best-in-class developers to build your next mobile application. We are a top-rated mobile app development company that delivers next-gen solutions for startups and medium-sized businesses.
Think of development languages like spoken languages. If you want to talk directly with someone, you must speak their language. That’s native development, apps communicate directly with the operating system. For Android, that means Java or Kotlin, and for iOS, Swift. No intermediary layer is required.
But what if you don’t have the time or resources to learn multiple languages or manage two different teams? That’s where cross-platform development comes in.
It allows developers to write a single codebase that works across platforms. However, because it relies on a “translator layer,” performance can sometimes take a slight hit.
A native vs cross-platform choice often comes down to resources. Native development usually requires more investment, while cross-platform solutions like React Native are more cost-friendly.
|
Factor |
React Native (Cross-Platform) |
Native Development |
|
Development Time |
Faster, single codebase |
Slower, separate code for iOS & Android |
|
Cost |
30–40% lower |
Higher, needs separate teams |
|
Performance |
Near-native, slight overhead |
Best-in-class performance |
|
UI/UX |
Good, but not 100% native |
Seamless, platform-optimized |
|
Scalability |
Flexible but sometimes limited |
Highly scalable with full control |
|
Languages |
JavaScript/TypeScript |
Java, Kotlin, Swift |
|
Libraries/APIs |
Rich, but with limits |
Full access to APIs and libraries |
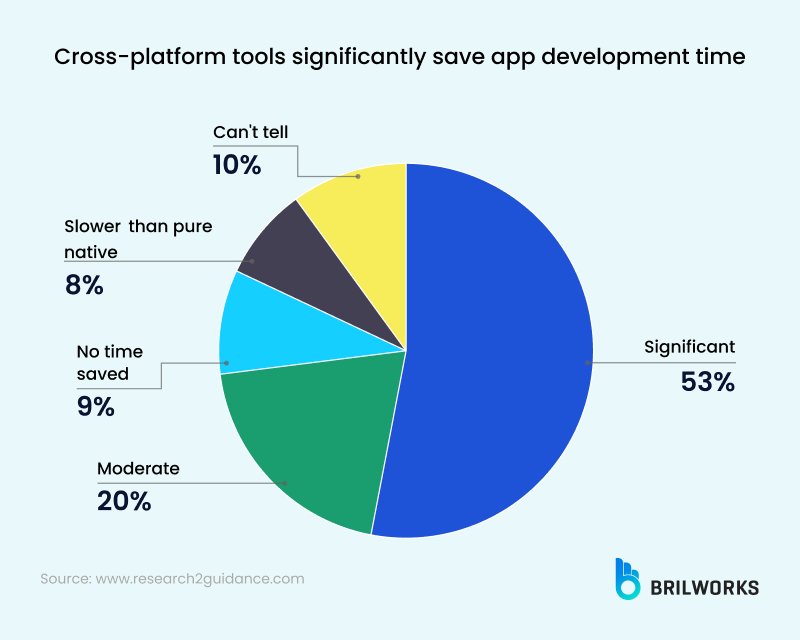
According to the Stack Overflow Developer Survey 2024, React Native remains the second most popular tool for mobile app development, admired by more than 55% of developers. Its continued adoption by mobile app development companies highlights its maturity as a framework.
Since it follows the cross-platform model, a single codebase can target both Android and iOS, reducing effort and cost. For a deeper look at what sets it apart, check out our detailed guide on What is React Native.
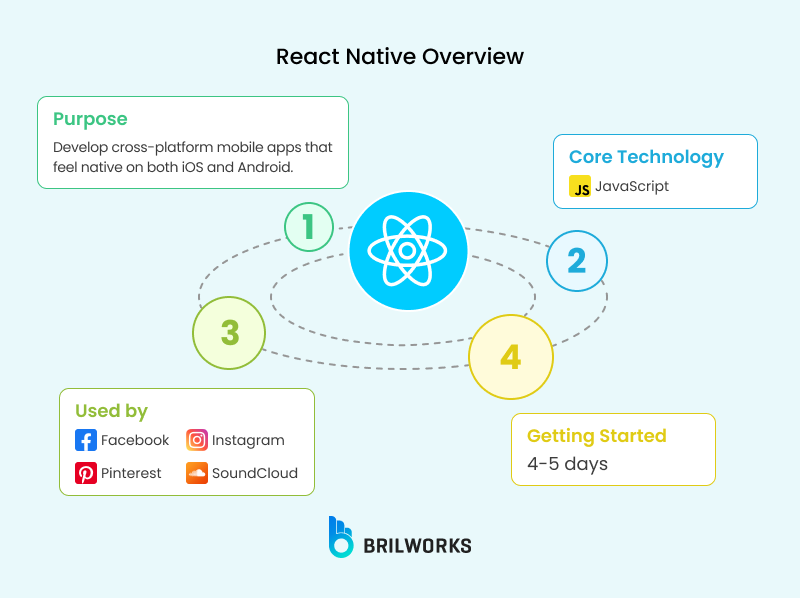
Launched as an internal project at Facebook in 2015 and released to developers in 2016, React Native has evolved into one of the most widely adopted frameworks for cross-platform apps. It relies on a JavaScript thread to control views and uses a bridge to connect with native APIs.
The result: faster development cycles and cost savings of up to 40–50%. By 2025, React Native has embraced TypeScript as the default language, further improving type safety and scalability.
Even world’s renowned companies have opted for React Native, from Facebook and Instagram to Pinterest and Discord. Here are some key reasons:
One team, one codebase, two platforms. This translates into reduced timelines and faster releases. According to a report by Kobiton, delays in mobile app releases cost companies over $100k annually. React Native minimizes such risks by accelerating development cycles.
Cross-platform apps can be 30–40% cheaper than native equivalents. Discord’s experience with React Native is telling, it helped the company save 30% in developing costs and was able to enjoy a 99% crash-free app.
Instead of choosing between Android or iOS, React Native lets businesses target both without extra cost. This wider reach can be crucial for startups and small businesses.
Up to 90% of code can be shared across platforms, reducing duplication. Some native coding may still be required, but React Native covers the majority.
Limited access to deep native modules.
Reliant on shared APIs and third-party libraries.
Some platform-specific features lag until libraries update.
Not all dependencies extend beyond Android and iOS.
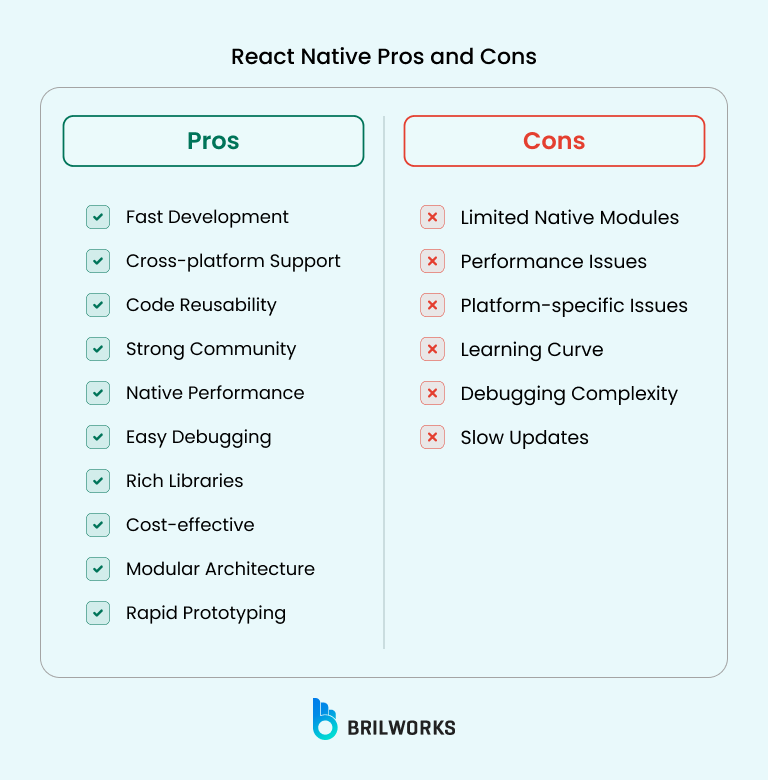
Native apps communicate directly with the operating system, ensuring speed and fluid performance.
Native apps can leverage every feature offered by the OS, from advanced sensors to custom animations.
Tighter integration with hardware encryption, secure APIs, and authentication features makes native apps less vulnerable.
Because they follow platform-specific design guidelines, native apps deliver a seamless, intuitive experience.
Higher development cost and longer timelines.
Requires separate teams for Android and iOS.
Can be a challenge for smaller businesses to sustain.
React Native wins here. A single codebase reduces duplication and speeds up delivery.
React Native development can cut costs by more than 30%. For budget-sensitive projects, it’s the practical choice.
Native remains unmatched for performance, fluid UI, and platform-optimized experiences.
Native offers more flexibility for long-term scalability, though React Native is catching up with frequent community updates.
React Native relies on JavaScript (or TypeScript), while Native requires Java or Kotlin for Android and Swift for iOS.
The choice depends on your project’s goals:
Use React Native if you need rapid development, lower cost, and wider reach, ideal for MVPs and startups.
Choose Native if performance, advanced security, and deep customization matter most, best for enterprise-grade apps.
Our experience as a React Native development company shows that React Native works exceptionally well for MVPs and moderately complex projects. For apps requiring deep native integrations or long-term scalability, native development remains the safer bet.
Both approaches have their place in modern mobile app development. React Native offers speed, cost savings, and cross-platform efficiency, while Native provides superior performance and deeper control.
Still unsure which approach suits your project? Partner with our team of experts. Whether you’re hiring React Native developers or evaluating the right stack, we’ll help you create the perfect solution.
No. Native apps always outperform cross-platform apps in raw speed, though React Native comes close.
React Native development can be 30–40% cheaper, especially when targeting both iOS and Android.
Most startups prefer React Native for MVPs due to lower cost and faster delivery.
It gets close but will never fully match native. For high-performance apps, native remains superior.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements