COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








Deciding between Vue and React in 2025 is a critical choice for any development team. The JavaScript ecosystem is massive, and these two titans sit at the top. React dominates the job market with its massive ecosystem, while Vue wins hearts with its gentle learning curve and out-of-the-box performance. This guide provides a head-to-head comparison of performance, jobs, and project suitability to help you choose wisely.
While some developers argue Vue makes development quicker, others say React’s TypeScript support is superior. Honestly, both sides have their points. What you pick isn't a small decision; it shapes how fast you move and how cleanly your project grows.
For those who need a quick answer, here's a high-level breakdown:
|
Feature |
Vue.js |
React.js |
|
Best For |
Startups, fast prototyping, mid-sized apps |
Large-scale enterprise apps, complex UIs |
|
Learning Curve |
Gentler, uses standard HTML templates |
Steeper, requires learning JSX |
|
Performance |
Excellent out-of-the-box reactivity |
Requires manual optimization for top speed |
|
Job Market |
Growing, strong in Asia/Europe |
Dominant, industry standard |
|
Mobile Dev |
Limited options (NativeScript) |
Mature solution (React Native) |
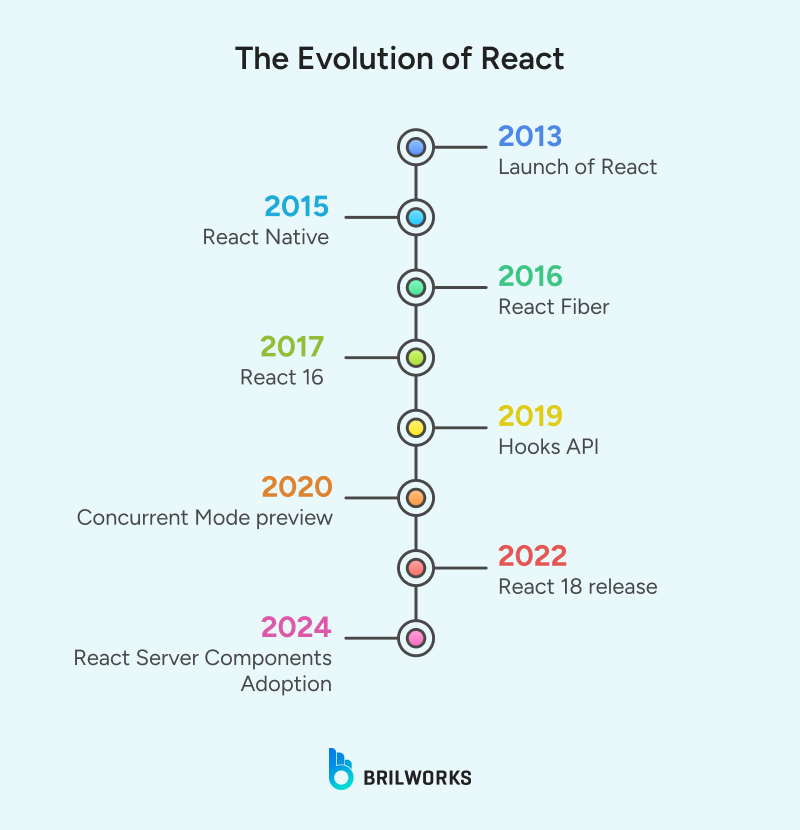
React is a popular open-source JavaScript library developed by a team at Meta in 2013 to build dynamic UIs for web apps. It uses a special syntax, JSX (JavaScript XML), which allows you to write HTML-like code directly within your JavaScript.
Maintained by a dedicated team at Meta and over 1,700 external contributors, React powers over 10 million websites globally, including those of Cloudflare, Dropbox, and Asana. According to Statista, it's used by nearly 40% of developers.
React introduced several concepts that have shaped modern frontend development, such as declarative UI, a virtual DOM, and its powerful component-based development model.
JSX: React's syntax extension, JSX, lets you write markup directly inside JavaScript, combining structure, logic, and behavior into a single, cohesive layer. This setup makes UI code easier to manage by reducing complexity rather than adding to it.
Mobile development: With React Native, you can create native iOS and Android apps using the same component model. This allows developers already familiar with React to transition into mobile development without a steep learning curve.
Versatility: React is incredibly flexible. It fits well with single-page applications, server-side rendering, and even desktop app development, integrating smoothly with a vast range of libraries and stacks.
Vue.js is a JavaScript framework that also follows a component-based, declarative model. Created by ex-Google engineer Evan You, Vue was designed to take the best ideas from React but make them lighter, more flexible, and easier to pick up. Unlike React's JavaScript-first approach, Vue leans more on standard web technologies: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
It supports declarative rendering using HTML-based templates and is described as "progressive," meaning you can start small and layer in more features as your application grows.
Gentle Learning Curve: Vue's biggest strength is its simplicity. With a basic knowledge of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, you can get started without complex tooling, making it approachable for beginners and teams that need to move fast.
Modular Architecture: Like React, Vue uses a component-based model where self-contained components can be reused across an application, making development and management much easier.
Rich Ecosystem: Vue comes with a rich set of official, out-of-the-box tools, including libraries for routing and state management. Its devtools also simplify debugging, so you don't have to stitch together third-party solutions to get started.
Because Vue was inspired by React, they share a lot of core concepts. If you've used one, picking up the other won't take long. Both use components, are declarative, and manage the UI with reactive data. Here are some key similarities:
JavaScript Core: Both are built on JavaScript and support TypeScript. React uses JSX to blend markup and logic, while Vue uses a template-based syntax that separates them more clearly.
Component-Based Architecture: Both frameworks break the UI into smaller, self-contained, and reusable components. This modular approach speeds up development and makes maintenance easier.
Virtual DOM: Both use a Virtual DOM to manage UI updates efficiently. Instead of manipulating the real DOM directly, they create a virtual copy, calculate the most efficient changes, and update only what's necessary.
Vue has a well-earned reputation for being beginner-friendly, largely thanks to its Single File Components (.vue files). These files organize your component into three familiar blocks:
<template>
<!-- Your HTML here -->
</template>
<script>
// Your JavaScript here
</script>
<style>
/* Your CSS here */
</style>This structure feels immediately recognizable if you've worked with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript before. React, on the other hand, uses JSX, which blends HTML-like syntax directly into JavaScript:
function Welcome() {
return (
<div className="greeting">
<h1>Hello, World!</h1>
</div>
);
}JSX is powerful, but it requires thinking in a more JavaScript-centric way from the start. For newcomers, it can feel like learning two things at once.
Vue also offers two ways to write components: the highly organized Options API, which is great for beginners, and the more flexible Composition API, which is closer to React's functional components with Hooks. React has standardized around Hooks (useState, useEffect), which are elegant but come with their own set of rules that require careful study.
Verdict: For a complete beginner, Vue tends to have a gentler onramp. If you're already a confident JavaScript developer, React's approach might click immediately.
Both React and Vue are fast enough for almost any application. The real difference lies in how they achieve that speed and what it means for developers.
React: Virtual DOM and Developer-Driven Optimization When state changes, React re-renders the component and its entire subtree by default. It then compares a new virtual DOM tree with the old one to calculate the minimal changes needed.
This is predictable, but it puts the onus on you, the developer, to optimize. You need to use tools like React.memo(), useMemo(), and useCallback() to prevent unnecessary re-renders.
In 2025, React Server Components (RSC) have also changed the game. RSCs render on the server and send only the resulting UI to the client, which can dramatically improve perceived performance but adds architectural complexity.
Vue: Reactive Performance Out of the Box Vue 3 uses a fine-grained reactivity system based on Proxies. It tracks exactly which components depend on which pieces of state.
When a specific piece of state changes, Vue knows precisely which components to update. This means Vue components are naturally performant.
Additionally, Vapor Mode, an upcoming compilation strategy, promises even more performance by compiling components into highly optimized JavaScript that manipulates the real DOM directly, eliminating virtual DOM overhead entirely for qualifying components.
Vue wins on practical performance ergonomics. Its reactivity system makes most code performant without manual intervention, which is a huge plus for teams that want to move quickly.
When it comes to popularity, React still leads the way. It's been around longer and benefits from a massive, active community. While Vue often scores higher in developer sentiment surveys like the State of JS, other indicators tell a different story.

Looking at the usage trends, and industry adoption, Reactjs dominates over Vuejs.
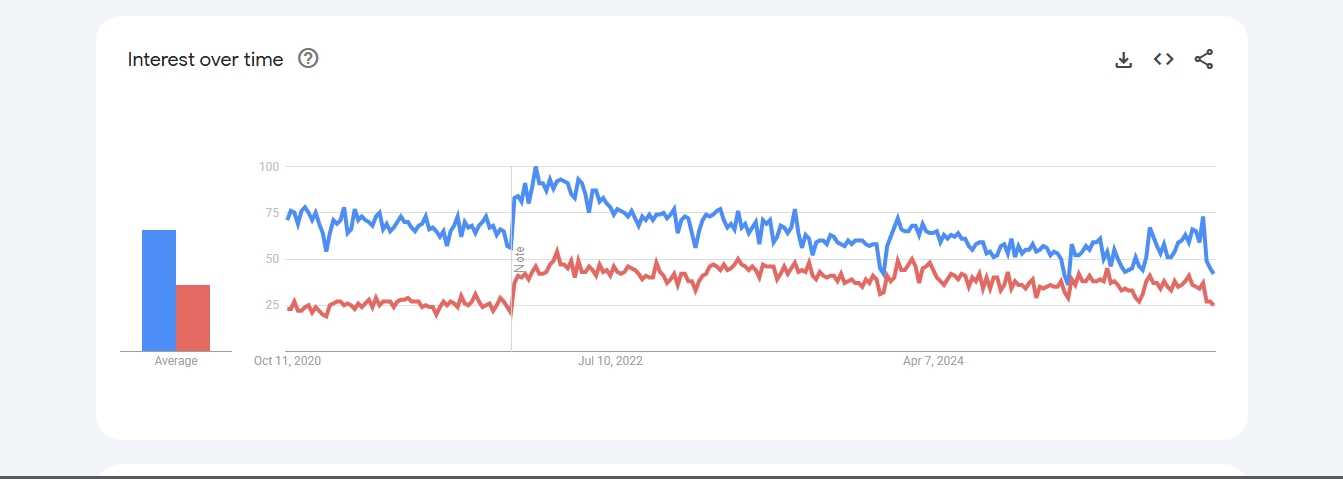
React.js is used by titans like Facebook, Netflix, and Uber.

That said, Vue isn't a niche player; big names like Adobe, GitLab, and Nintendo use it. Still, its overall market footprint doesn't quite match React's, at least not yet.

React has a clear lead in market share and job availability, especially for enterprise-grade roles.
Both frameworks can scale, but their design philosophies make them better suited for different types of projects.
Use Vue when:
Your team wants faster development cycles and rapid prototyping.
Simpler state management is a priority.
The development team is more familiar with traditional HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
You are building mid-sized applications where out-of-the-box performance is key.
Use React when:
You're building a complex, large-scale application that will grow over time.
Cross-team collaboration demands a consistent and strict architectural pattern.
You need access to the largest possible ecosystem of tools and libraries.
The project involves complex state interactions and large data sets.
React has a clear advantage here with React Native, a mature and widely adopted solution for building truly native apps using React components. You can often reuse logic and components between your web and mobile apps, saving significant time and effort.
Vue's options are less mature. While tools like NativeScript-Vue exist, they have smaller communities and are not as widely adopted as React Native.
Verdict: For serious mobile development, React is the undisputed winner.
|
Vue.js |
React.js |
|
Pros |
Pros |
|
Built-in transitions and component caching |
Mature ecosystem with deep enterprise integrations |
|
Better handling of prop/attribute inheritance |
Full flexibility with state management and rendering |
|
Simplified event and data flow with v-model |
Granular control over component internals with hooks |
|
Powerful dynamic component design with slots |
JSX allows full control inside your render logic |
|
Clear separation of concerns in .vue files |
Rich third-party libraries (e.g., Framer Motion) |
|
Cons |
Cons |
|
Slightly smaller ecosystem for advanced plugins |
No built-in animation or caching—requires libraries |
|
Multiple ways to write logic can confuse beginners |
useEffect complexity can lead to mismanaged side effects |
|
"Magic" abstractions can make errors hard to trace |
JSX boilerplate for simple things like inputs/classes |
|
Opinionated defaults can limit flexibility |
Re-rendering requires manual optimization |
The React vs Vue debate isn't ending anytime soon. Both are phenomenal JavaScript frameworks that keep improving with each release, often borrowing strengths from one another.
If you're already into React, Vue is definitely worth exploring. Knowing both gives you incredible flexibility, and a mix of ideas from each can lead to better apps.
If you're leading a project and this choice matters, we can help. Our team offers free guidance to help you pick a tech stack that aligns with your goals. We also offer full-stack React development, app modernization, and help with building dedicated teams. Just share a few details, and we'll get in touch. To start your journey, consider reaching out to a Hire a React.js development team.
For 2025, the best choice depends on your project. React remains the industry standard for large, complex applications due to its massive ecosystem and talent pool. Vue is often preferred for its faster development speed and gentler learning curve, making it ideal for startups, mid-sized projects, and rapid prototyping.
Vue has a significantly gentler learning curve. Its syntax is based on standard HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which is intuitive for most developers. React requires learning JSX and understanding more complex state management concepts from the start, making its initial curve steeper.
Both are excellent for dynamic UIs. Vue offers a highly optimized reactivity system out-of-the-box that automatically tracks changes and updates the DOM with high efficiency. React uses a Virtual DOM, which is also extremely fast, but often requires manual performance optimizations (like React.memo) in complex applications.
In 2025, React continues to hold the larger global market share, dominating in North America and enterprise-level jobs. However, Vue has seen explosive growth, particularly in Asia and Europe, and often scores higher in developer satisfaction surveys, indicating a strong and expanding user base.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements