COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








If you're building a modern web app, chances are you've already thought about React. If not, your team probably has. It's backed by Meta, powers tons of websites globally, and gives you the flexibility to avoid those "why did we do that?" moments later on.
React was built by Facebook, sure. But today, we can see it behind several popular brands' websites, such as Netflix, Airbnb, NASA, and tens of millions of other sites. According to Statista's 2024 survey, it's the second most-used web library in the world. There are so many good reasons behind its popularity. It perfectly balances developer-friendly design with impressive scalability.
React offers impressive speed, making it an excellent addition to your tech stack. Whether you're working on a small side project or managing something complex, an enterprise frontend, React ships almost everything a developer may need to build modern, complex user-interfaces. In this post, we will explore the genuine reasons why React is popular and when to use it.
React (or React.js or ReactJS) is an open-source JavaScript library,
that is used to build fast, interactive user interfaces. Created at Facebook, React quickly transformed how developers think about frontends. It lets developers build applications (website user interfaces) out of small, reusable components.
The component can be a small, basic button or something complex, a layout that contains its own logic. React's rendering technique through virtual DOM is quite popular. Instead of manipulating real DOM every time, React updates a lightweight copy (or virtual DOM) first. Then it figures out the changes and then updates the real DOM.
If you're building a modern web app, chances are you've already thought about React. If not, your team probably has. It's backed by Meta, powers tons of websites globally, and gives you the flexibility to avoid those "why did we do that?" moments later on.
React was built by Facebook, sure. But today, we can see it behind several popular brands' websites, such as Netflix, Airbnb, NASA, and tens of millions of other sites. According to Statista's 2024 survey, it's the second most-used web library in the world. There are so many good reasons behind its popularity. It perfectly balances developer-friendly design with impressive scalability.

React offers impressive speed, making it an excellent addition to your tech stack. Whether you're working on a small side project or managing something complex, an enterprise frontend, React ships almost everything a developer may need to build modern, complex user-interfaces. In this post, we will explore the genuine reasons why React is popular and when to use it.
React (or React.js or ReactJS) is an open-source JavaScript library,
that is used to build fast, interactive user interfaces. Created at Facebook, React quickly transformed how developers think about frontends. It lets developers build applications (website user interfaces) out of small, reusable components.
The component can be a small, basic button or something complex, a layout that contains its own logic. React's rendering technique through virtual DOM is quite popular. Instead of manipulating real DOM every time, React updates a lightweight copy (or virtual DOM) first. Then it figures out the changes and then updates the real DOM.
There are so many frameworks exist today, but not as mature as React. It has been used for a decade, from small to large-scale projects. Here's what React benefits provide to developers, and where it demands a little care.
React's component-based model means developers can build UI in independent blocks. For example, many developers can work on different aspects of a single project without stepping on each other's toes. Let's say a React development company plans to build a UI, it can onboard multiple developers to work on different parts, like a specific widget or a dashboard page of the app.
This is a popular approach that many companies follow today. Plus, this way, developers can speed up development work. If you are aware of Reactjs optimization techniques, you can make your app even faster using methods like code splitting and lazy loading. You can definitely go with Reactjs, if you want something to go faster.
That said, React doesn't magically make your app fast. Poor state management, over-rendering, or excessive use of dependencies can negatively impact overall performance, no matter what library you use.
React offers a great level of flexibility. Developers can choose their preferred tools and design applications. However, this flexibility can lead to inconsistent development. Well, it is the development team's responsibility to establish rules and guidelines, rather than relying solely on the framework. With standard development practices, React makes it easy to build products, all without adding a bunch of technical debt.
The Virtual DOM provides a practical advantage. React keeps interfaces responsive by updating only the changed elements, even with complex state updates. Combining this with server-side rendering (SSR) can improve SEO and performance, crucial for apps reliant on traffic and conversions.
However, SSR can make deployment complex and put a load on the server. Therefore, it is not always the best choice. React offers options, so careful consideration is necessary. These decisions are the developers' job.
React has a relatively low barrier to entry. If you know JavaScript and ES6, and can grasp JSX, you're already 70% of the way there. Compared to Angular, with its many concepts, or Vue, which has stronger opinions, React allows developers to grow into it gradually.
You can build something useful in a weekend or something enterprise-grade over a year, and the transition between the two isn't difficult. That's why it's often the first framework new front-end developers learn and the one they stick with when projects become serious.
Reusable components are the backbone of React development. Not because it's trendy, but because once you've built a clean, self-contained Button or Modal, you can use it everywhere. React pioneered this approach. However, a word of caution: unintentional reuse results in a fragile design system.
Avoid "one-size-fits-all" components that expand into hundreds of lines of prop management. Prioritize thoughtful reuse over default reuse.
React's long-term advantage lies in React Native. It leverages the same principles to create native mobile apps for iOS and Android from a single codebase. However, React Native is more than just "React for mobile." You'll still need to learn mobile APIs, platform-specific nuances, and potentially some native bridging.
Yet, if your team is already familiar with React, the learning curve is reduced. This is a substantial advantage for startups aiming to launch web and mobile MVPs without expanding their workforce.
React has been around long enough to prove it's not just a trend. It's still the go-to choice for more than 1/3 of professional JavaScript developers for frontend development. Here's why it continues to grow, even when there are other modern alternatives.
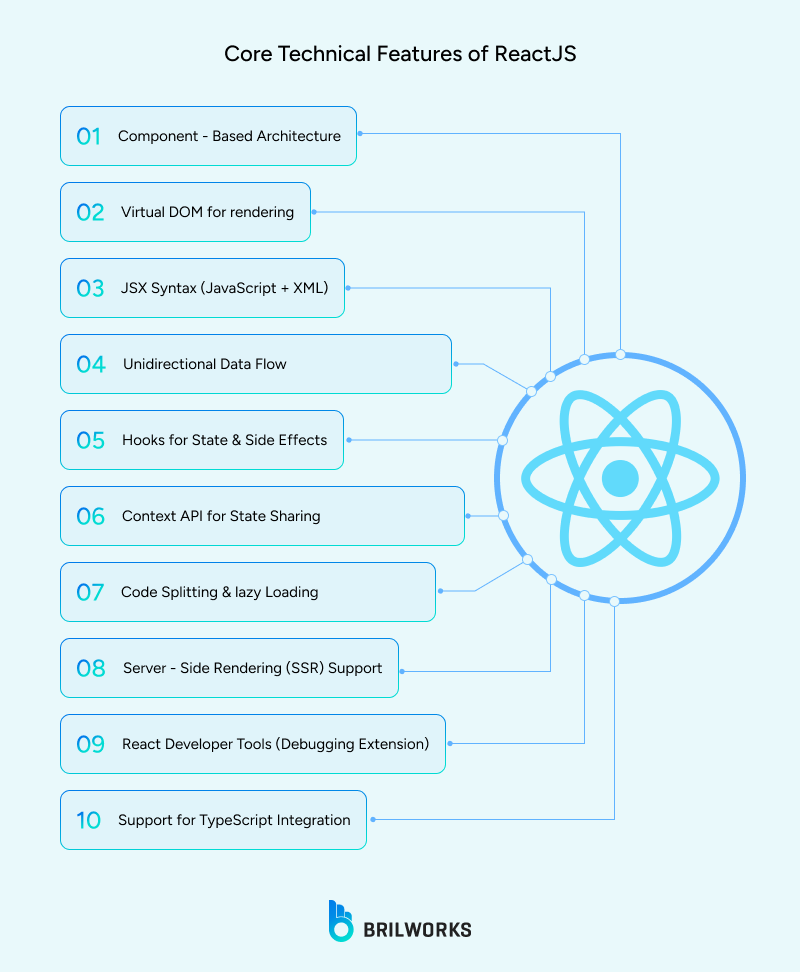
React's declarative component model makes it easy to build user interfaces. Developers can describe how the UI should look based on the current application state, and React takes care of rendering the correct output.
React uses JSX (JavaScript XML), a syntax extension that allows developers to write HTML-like code directly in JavaScript. This way, React makes it easier to build custom, reusable components. JSX also accepts HTML quoting and supports embedding other components.
React promotes keeping internal logic decoupled - it minimizes the time refactoring or duplicating functionality. This also makes it less prone to breaking after updates that can occur quite often in large applications.
Provided developers do not make too much duplication in the internal logic, the app is cleaner when it scales. It can be more easily tested and maintained. Developers can continue to build at the same pace, in most cases, even at scale.
React's Virtual DOM serves as an in-memory representation of the actual DOM and does a "diff" to only identify and make the minimum amount of changes before updating to the real DOM. This method can reduce costly reflows and repaints to make your interfaces more performant.
With each atomic change in the state of an application, performance could be negatively affected with the sluggishness of the real DOM rendering alone; instead, React lets you mill activity through a lightweight layer of updates and remains responsive in contrast to tediousness even in the most complex applications.
React has one of the most active developer communities. Developers benefit from their active user base, having 238K+ GitHub stars, countless answered questions on Stack Overflow, and not to mention endless updates from the open-source community, which allows a developer to almost always avoid getting stuck.
This also results in better documentation, faster response time on bug fixes, and a large ecosystem of third-party applications.
React functions via a unidirection data flow, indicating that any changes to a child component do not directly affect its parent components. This escalates state and data flow more predictable, especially as application scale grows. It also reduces bugs from unexpected changes in component interaction, therefore, increasing stability.
Many enterprise level clients, such as Netflix, Airbnb, Uber, PayPal, Instagram, Walmart, and NASA, use it (or React Native) in Production environments.
React has a powerful testing ecosystem. Tools such as Jest, Enzyme, and React Testing Library, make it easier to simulate user interactions, track how components behave, and find bugs earlier. Testing React components is also very easy due to the modular structure of the components and the consistent output.
React's ecosystem is packed with plugins, from VS Code plugins to debugging tools in a browser. There are tons of tools that improve the experience of the developer. Tools that help with everything from auto-completions, linting, live component tracing to visualization of states in redux.
React's Hooks API (such as useState, useEffect, and useReducer) has changed the way developers manage state and side-effects in functional components and has replaced the need for class components in many places. For larger apps, using tools such as Context API or Redux offers effective means of handling global state, providing global control with minimal re-rendering.
ReactJS is not a one-size-fits-all solution—but for many modern development needs, it proves to be an exceptionally strong fit. Its flexibility, performance capabilities, and cross-platform reach make it ideal for a wide range of real-world scenarios.
For applications that rely heavily on interactive, dynamic content, React’s component-driven architecture provides the control to manage frequent updates while maintaining performance.
Consider the following: features such as real-time notifications, drag-and-drop implementations, and live data visualizations are perfect examples of types of features that benefit from React’s efficient rendering engine. Based on this, React is an excellent choice for real-time dashboards, collaborative tools, and single-page applications (SPAs).
Scalability was a major consideration of React during its design. The modularity of React means that breaking a large application into reusable, isolated components is simple and straightforward, allowing teams to scale without having to pay the price of rewriting code and limiting the architecture.
React helps to maintain consistency across teams and features no matter the size of the application, from growing startups to large enterprise applications, even as the application continues to grow.
Applications that handle heavy data transactions, and need near-instant response from the UI (e.g., financial dashboards, monitoring solutions, logistics applications) will benefit from React's Virtual DOM representation of the HTML to be rendered on the client's DOM and the usage of diffing algorithms that minimize costly DOM manipulation. As the application and UI become more complex, performance can remain consistent with the same event cycle.
React isn't limited to the browser. With React Native, developers can use the same core design principles to build native mobile applications for Android and iOS. For desktop environments, React Desktop allows for similar cross-platform consistency. This reuse of logic and design patterns helps businesses accelerate time-to-market across multiple platforms, without maintaining entirely separate codebases.

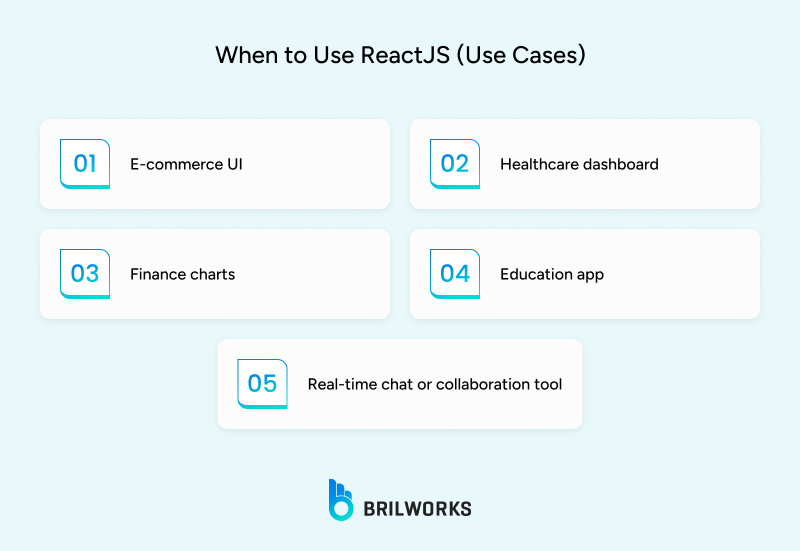
React's flexibility makes it popular across diverse sectors:
ReactJS has not gained its popularity based on hype, but rather on providing solutions to real-world front-end development problems. React is relatively simple to use and has a low learning curve for teams of any size.
You can use it for building dashboards, e-commerce site, cross platform mobile app, and different kinds of applications. Overall, this is a wise decison to choose Reactjs if you already have a JavaScript team or want to build an app with limited budget. Finding and hiring Reactjs developers relatively easy. Therefore, if you are considering a new application or re-thinking your tech stack, ReactJS is definitely worth consideration. To get the best performance from React, ideally you would want to hire experienced reactJS developers and/or consultants, so that you can develop better/faster while leveraging all of the benefits of using ReactJS, while feeling confident about the decision.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements