COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








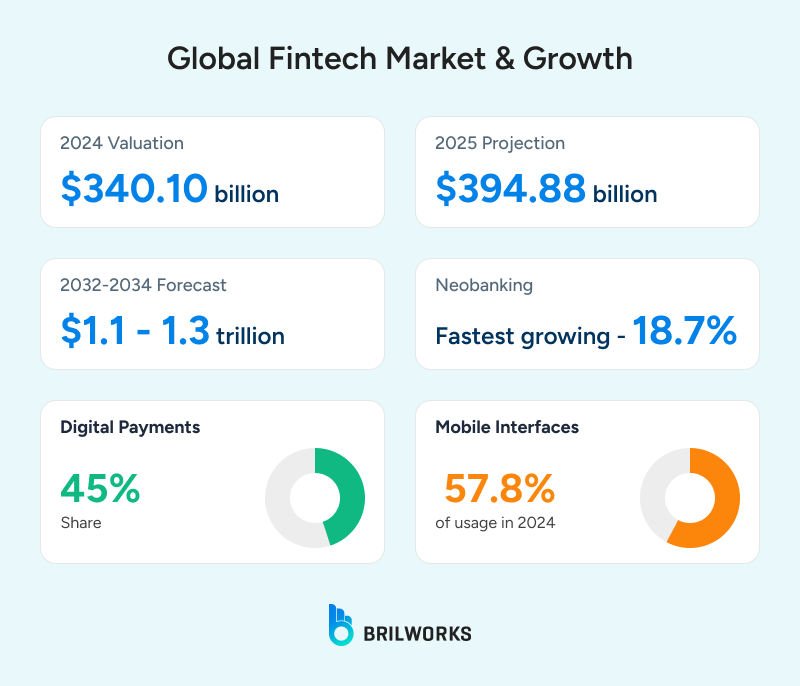
Fintech has quickly moved from a niche space to a central part of how people pay, invest, and borrow. Digital finance has now woven into our everyday lives. In fact, fintech has been one of the fastest-moving tech sectors, with global investment reaching $394 billion in 2025. In India, for example, over 300 million people now use UPI monthly. In the U.S., more than half of all consumers manage their finances using mobile apps.
Over time, user expectations have also changed. Speed and security are no longer extras; they’re baseline. While there is an abundance of technologies to develop finance apps, fintech apps require more than UI and performance. Security is non-negotiable, and therefore, developers face many challenges when it comes to building apps related to finance and money management.
ReactJS is one of the most popular libraries for building UIs, whether for fintech, healthcare, SaaS, or social platforms. The library is used to build different types of apps. If you are considering going with React for your next fintech development project, then this article is for you. In this article, we will share some practical insights on how to use React in a fintech project, what to consider, and some solutions to the challenges that may appear during development.
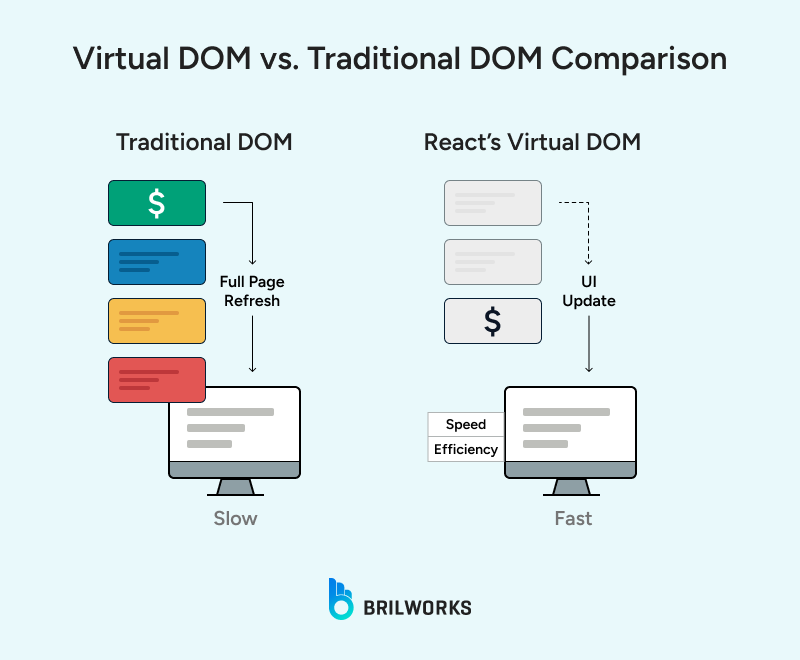
Back when fintech apps were new to users, most of the apps had some basic features, letting people check their balance, pay a bill, and track spending, but in the last 10 years, a lot has changed, including the fintech industry. React was launched as a library to build captivating, dynamic front-ends that could change state without loading the entire page.
It was used by Meta, Netflix, and many big names, including Coinbase. Today, it can be seen behind millions of web applications worldwide. In fact, it is the second most popular library in the world for building user interfaces.
Fintech apps don’t usually get built all at once. There’s always something in review, or waiting on legal, or being tested on a small group of users. React is well-suited for this kind of stop-and-go development.
You could update one part of the app without touching the rest. You didn’t need to pause development just because the backend wasn’t ready. That kind of flexibility isn’t unique to React; you can find the same level of flexibility in many popular front-end development libraries and frameworks, too. But React has been through a wide range of use cases and continues to hold up without getting in the way.
You can choose React if you favor modular development, where you can involve multiple experts to work on specific parts of the application. Building apps in fragments is a common practice in large-scale projects. Let’s briefly explore some advantages of React in Fintech app development.
See Also: Why Java Is Still Popular in Fintech
Modern fintech dashboards usually aim for ultra‑quick response, loading in under ~2 s. React’s rendering speed outpaces many popular front-end frameworks. In addition, it brings measurable frontend advantages in fintech contexts:
A fintech app must be vertically scalable. When you add more and more features over time, the process should not break or slow down. React doesn’t solve that for you, but it gives teams a structure where changes can stay local.
For instance, take a lending app that starts with a basic loan application form. Over time, the team wants to add more to that same screen: EMI calculators, credit score graphs, repayment schedules, and real-time offers. That’s vertical growth, it’s not new pages, it’s more functionality in the same flow.
With React, each of these new features can be built as a separate component. One team can work on the credit graph while another handles repayment logic, without touching the main loan form. Since components manage their own state and UI logic, changes stay limited to their own scope.
This means updates don’t ripple across unrelated parts of the app, which is especially important when each piece is backed by different data and timing. It doesn’t remove the complexity. But it does contain it.
Major trading platforms stream live market data without refresh. Delays make users second-guess the numbers on screen. React doesn’t fetch the data, but it handles what comes next. When a transaction posts or a price ticks, React updates only the part of the interface that needs to change. That keeps the app light, even when data updates are frequent. Paired with tools like WebSockets or React Query, teams can handle high-frequency feeds without redrawing the whole UI.
According to recent research, nearly 42% of data breaches in top fintech companies trace back to third-party vendors. These incidents underscore a key risk area fintech developers can’t ignore: external dependencies and UI-level controls play a real role in compliance and data safety.
Here’s how to solve some of the most common issues developers face in this space.
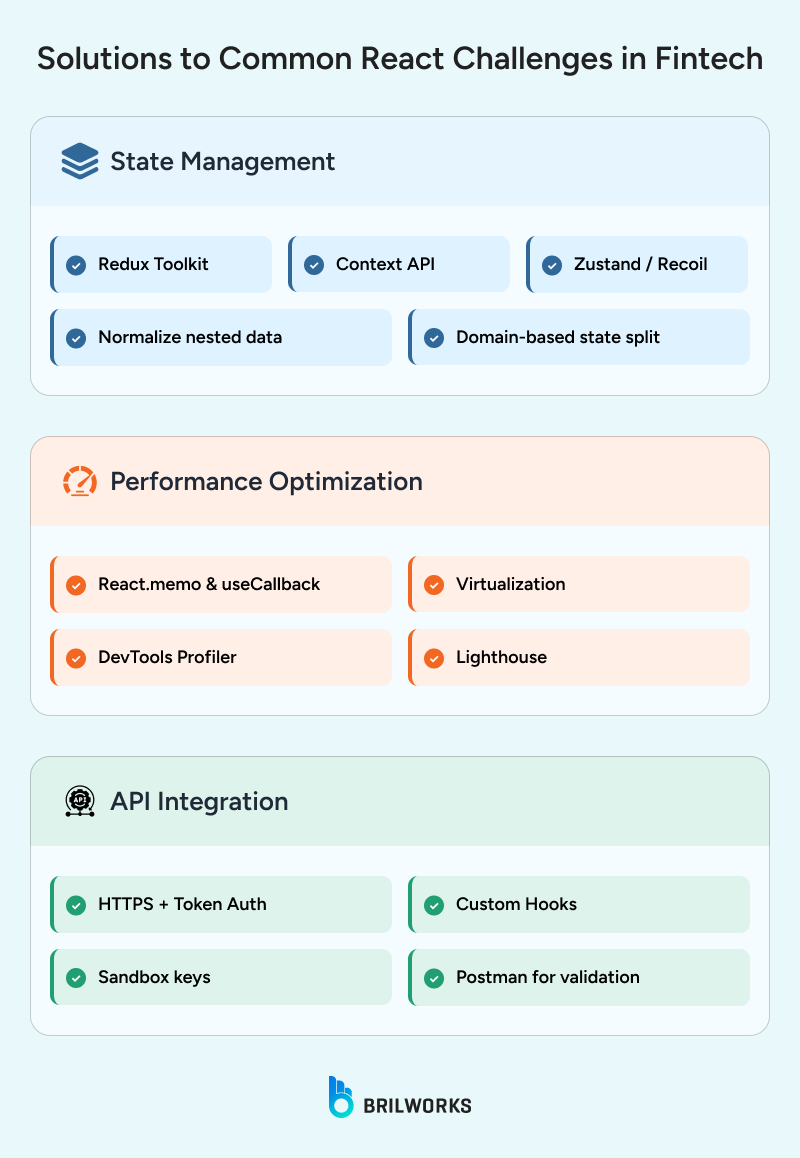
Fintech apps often involve deeply nested data, making state management tricky. You can make this process smooth by choosing the right state management strategy. Check out the best Reactjs state management libraries that you can use to handle state management. Below are tips to handle state management in complex UIs.
Another challenge is performance bottlenecks. Here are some common bottlenecks and fixes
Below are the techniques to optimize your app's performance.
In our article React.js performance optimization, we have compiled some best practices that developers should follow to build a highly performant app. In addition, there are some tools that you can use to find out performance-related issues.

Structure your React code around features, not just pages or UI elements. Group components, hooks, and styles by the domain they serve (e.g., payments, analytics, user settings). This keeps the codebase organized as your app scales and teams grow.
Keep things like form inputs, authentication flows, or KYC data entry in controlled components. It makes the data flow easier to monitor, validate, and secure, especially when handling sensitive financial information.
Avoid scattering session data like auth tokens or user roles across components. Use React Context or lightweight state libraries like Zustand to manage it centrally, so it’s easy to enforce rules and wipe sensitive data when needed.
Use route guards to protect sensitive screens. With React Router v6, you can define roles (like admin, user, auditor) and only show routes based on the current user’s permissions. This helps avoid accidental access to restricted views.
Wrap all outgoing requests with Axios interceptors to automatically attach tokens, handle session expiration, and catch unauthorized access in one place. It’s cleaner than repeating logic across every fetch.
Financial data needs to stay fresh. Tools like SWR or React Query work well with React.Suspense to fetch, cache, and auto-refresh data, keeping dashboards up to date without you writing a ton of boilerplate.
Performance matters in fintech, especially with fast-changing values like stock prices or charts. Use useMemo, useCallback, or React.memo to prevent unnecessary re-renders and keep the UI smooth.
Wrap all your business logic (taxes, interest, currency conversions) in testable functions, and write unit tests to make sure they work exactly as expected.
Track actions like rapid transfers, repeated failed logins, or IP changes using behavior analytics. These patterns can be early signs of fraud, and logging them helps build preventive systems down the line.
Don’t assume encryption is working, test it. Before going live, verify that sensitive data (like user credentials or transaction details) is encrypted during transmission and never stored in plain text.
React is one of the core technologies of modern fintech platforms that integrate A capabilities. From intelligent chatbots to fraud detection dashboards, React is proving essential in bridging complex backends with responsive, intuitive frontends.
React pairs well with libraries like Recharts, D3.js, or Chart.js to deliver high-performance, interactive charts that visualize everything from real-time stock trends to historical loan repayment patterns. When combined with tools like React Query or SWR, these charts update seamlessly as fresh data streams in from AI-backed APIs.
|
Feature |
Traditional React Fintech App |
AI-Enhanced React Fintech App |
|
User Experience |
Manual, rule-based interactions |
Predictive, conversational, adaptive |
|
Fraud Monitoring UI |
Static alerts |
Live anomaly heatmaps, behavioral cues |
|
Investment Suggestions |
User-driven research |
AI-generated recommendations |
|
Credit Analysis |
Form-based input, slow decisions |
Instant AI-backed scoring + feedback |
|
Data Visualization |
Static charts |
Live, real-time charts with ML input |
|
Personalization |
Generic UI |
Context-aware, user-specific interfaces |
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored what it takes to build modern fintech platforms with React. We’ve also looked at how frontend trends and AI are reshaping the fintech domain.
Whether you’re evaluating your current setup or exploring what’s possible, this is the point where clarity matters more than complexity. If at any stage you need support, from architectural decisions to scaling ReactJS development, Brilworks can help. We work with fintech teams to strengthen delivery with domain-aligned ReactJS developers who understand both speed and precision.
React’s component reusability, rich ecosystem of libraries, and strong developer tooling enable teams to build and iterate faster, reducing the time spent on repetitive UI tasks and allowing fintech products to launch quicker than with traditional frameworks.
React works seamlessly with AI libraries like TensorFlow.js and can visualize model outputs using tools like D3 or Recharts, making it well-suited for displaying predictive financial insights in real-time, interactive dashboards.
Beyond HTTPS, fintech applications built with React should enforce secure authentication (like OAuth or JWT), encrypt sensitive data in transit and at rest, validate all inputs rigorously, and guard against XSS, CSRF, and other client-side vulnerabilities.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements