COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








Whether your business is in sales, finance, or any other field, chances are you're already using some SaaS. Today, almost no business can operate without Software as a Service, or SaaS. These tools are everywhere. They've changed the way businesses handle their operations.
Developers frequently leverage these services to enable communication between different internal and third-party software. For example, if you are creating a payment app, you will integrate payment gateways. If you're building an analytics tool, you may need Google Analytics, Power BI, and CRM platforms like Salesforce.
But this integration isn't always easy. Developers often share their struggles on forums and tech communities. SaaS integration challenges are very common, which is why understanding them is important. In this article, we'll explore some of the main challenges businesses face when integrating SaaS tools.
From building new SaaS apps to upgrading established platforms, our saas development services deliver scalable solutions tailored to your business goals and user expectations.
It is the process of connecting different cloud-based applications so they can work together. Major software/business tools utilize several SaaS tools for different kinds of functions, like customer relationship management, marketing, accounting, and operations.
The very obvious thing is that SaaS integration helps you get the most out of your technology investment. Every third-party service is created to support developers. They provide many benefits, depending on how you use them. They let your systems work together in ways you couldn't manage manually.
They turn disconnected tools into a network that automates real business outcomes. Take an example of a third-party HR service that a business can use to trigger messages to the facilities system.
SaaS integration directly impacts business operations. The right integrations are useful in ways that matter for the business.
SaaS integration always brings new challenges to organizations. By recognizing challenges up-front, teams are better prepared to plan for them and minimize costly decisions.

Integrations can create new points of vulnerability if not handled carefully. Data moves across systems, and each connection can become an attack vector. Meeting regulatory requirements adds another layer of complexity.
Common security risks:
Poorly designed integrations make systems slow, or they can even fail when there is a high load. This is very common among businesses; when the users grow, the system becomes unreliable. Below are some performance-related issues that may occur due to improper integration.
|
Feature |
Scalable Approach |
Non-Scalable Approach |
|
API design |
Asynchronous, rate-limited, fault-tolerant |
Synchronous calls, no throttling |
|
Data handling |
Batched or event-driven processing |
Real-time heavy load without optimization |
|
Error management |
Retry mechanisms and monitoring |
Errors break the workflow |
Many complex integrations (e.g., ERP, CRM, legacy system integration) need advanced, specialized technical skills. Many companies don't have those skills inside their team, so projects slow down, or they have to rely on outside help. Let's take a look at some critical skills a developer should have when it comes to integrating complex systems.
Take an example; if a company's digital infrastructure is created around Salesforce's proprietary API, it will be challenging for them to move to another CRM, making them rebuild almost the entire system. Another example is Apple's ecosystem. There are numerous services that limit flexibility and make switching costly. Some common risks are:
|
Feature |
Open Integration |
Closed Integration |
|
Flexibility |
Can switch vendors easily |
Tied to specific vendor tools |
|
Cost |
Lower long-term switching cost |
High cost to move or adapt |
|
Future-proofing |
Easier to adapt to new tools |
Limited to vendor roadmap |
iPaaS tools make it simple to connect different apps without writing complex code. You can build workflows with drag-and-drop tools, use ready-made connectors for popular apps, and keep an eye on how everything runs. Here are some of the well-known platforms you can try.
Here's what you need to consider when selecting a platform.
API management tools help control how APIs are used, keep them secure, and ensure they perform under load.
Core concepts:
Essential capabilities:
Phased integration helps reduce the risks of connecting everything in one go. Teams can start with the most important systems first and smoothly handle the time when old and new systems run together.
Step-by-step approach:
|
Approach |
Benefits |
Risks |
|
Incremental |
Easier to manage, fewer disruptions, faster feedback |
Longer project timeline |
|
All-at-once |
Immediate full integration |
High risk of errors, hard to troubleshoot, major downtime |
Continuous testing helps make sure integrations keep working as systems evolve. With proper monitoring, teams can spot and fix issues before they cause any disruption.
Key monitoring metrics:
Automation tips:
Compliance should be part of the integration design from the start. Developers should have a clear idea of data movement, where to store it, and who can access it.
Essential measures:
You can align integration with specific goals. To define business, you need to have clarity on your business issues. Once your goals are clear, you can ask yourself before setting up an integration process.
This will help you define business objectives.
There are so many tools, technologies, and programming languages. Many professionals may feel overwhelmed when there is too much on their plates. But, without the right tool, your team may face several issues just because you have only decided on the basis of popularity. Evaluate different tools against each other before making a decision.
|
Approach |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Custom Dev |
Fully tailored |
High cost, maintenance |
|
iPaaS |
Quick deployment, pre-built connectors |
Subscription cost |
|
Middleware |
Flexible, reusable |
Requires setup, monitoring |
Security is non-negotiable. A developer must know the latest security protocols, how to secure different integration points, and add encryption and authentication mechanisms to create a secure architecture. Below are the practices that you must not avoid.
Document data flows, mappings, error handling, and dependencies. Use tools or templates for consistency.
Roll out integrations gradually, test each stage, and have rollback plans. Train users on new workflows.
Track KPIs like sync failures, API response times, and throughput. Continuously identify bottlenecks and improve performance.
SaaS integration is evolving rapidly. Modern tools and smarter methods are transforming how businesses connect their systems and put their data to better use.
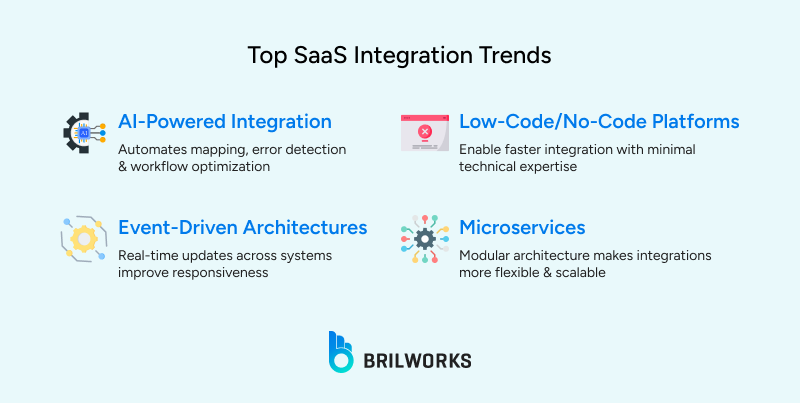
These trends help solve challenges like complexity, scalability, and data consistency, while opening up new ways for businesses to work faster and make smarter decisions.
Integration is not just a technical task. It's a foundation for better operations and smarter decisions. Businesses that invest in thoughtful, well-architected integrations reduce errors, save time, and make data more actionable.
Brilworks helps organizations implement integration strategies that align with business goals, ensure security, and scale with growth. Robust integrations provide long-term benefits: consistent workflows, reliable data, and the ability to adapt quickly as systems evolve.
To optimize your SaaS integrations, Brilworks offers hands-on support, proven frameworks, and secure, scalable architectures. Investing in robust integration now pays off with consistent workflows, fewer errors.
Compare time saved on manual tasks, reduced errors, and faster decision-making against implementation costs and ongoing maintenance. This gives a clear picture of actual value.
Use an agile integration approach with regular checkpoints. Ensure your architecture can adapt to changes without needing a full rebuild.
Generative AI can speed up integration by automatically mapping data, suggesting better ways to connect systems, and spotting issues early through pattern analysis. This helps teams fix problems faster and with less manual effort.
Implement end-to-end encryption, strong authentication, regular audits, and strict access controls. Keep detailed logs of all integration activity for accountability.
Most enterprise projects take 3–6 months, depending on system complexity, number of integrations, data volume, and organizational readiness.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements