COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








This guide explores how to build scalable ReactJS applications using best practices, performance optimization techniques, and clean architecture. From understanding core concepts and project structure to implementing advanced tools like Next.js, you will learn what it takes to develop ReactJS apps that grow seamlessly with your business.
React.js remains one of the most widely adopted front-end JavaScript libraries in 2025, powering a significant portion of the web.
According to the Stack Overflow survey 2025, over 44% of professional developers prefer React for web development. JavaScript frameworks and libraries continue to dominate the industry, with JavaScript remaining the most popular programming language overall. This underscores the importance of ReactJS in modern development.
At its core, React JS is a powerful library for building fast, scalable, and maintainable user interfaces.
React’s architecture allows large applications to scale efficiently:

1.Component-Based Architecture
Modular components simplify managing large codebases and enable multiple developers to work on different features simultaneously.
2. Efficient Rendering with Virtual DOM
Updates only the changed parts of the DOM, keeping UIs responsive even for complex applications.
3. State Management & Scalability Patterns
Solutions like Redux, Flux, or built-in React hooks centralize state management. Micro frontends allow independent development, deployment, and scaling of UI segments.
4. Performance Optimization Techniques
8. Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
Improves load speed and SEO by rendering components on the server before sending them to the client.
9. Future-Proof Scalability
Supports backend integrations and microservices, allowing applications to handle increased traffic without performance degradation.
10. Developer Experience and Maintenance
Clear separation of concerns, extensive tooling, and community support make onboarding easier and development faster
Establishing a strong foundation ensures maintainable and performant apps:
1. Project Structure
Organize folders by feature rather than file type. For example, /UserProfile can include its own components, containers, and utils.
2. State Management [Redux vs Context API]:
3. Code Splitting with React.lazy and Suspense
Load components dynamically for faster initial load.
const Dashboard = React.lazy(() => import('./Dashboard'));
function App() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<Spinner />}>
<Dashboard />
</Suspense>
);
}4. Testing with Jest and React Testing Library
Ensure every change is reliable.
import { render, screen, fireEvent } from '@testing-library/react';
import LoginForm from './LoginForm';
test('submits the form when both fields are filled', () => {
render(<LoginForm />);
fireEvent.change(screen.getByLabelText(/username/i), { target: { value: 'jane' } });
fireEvent.change(screen.getByLabelText(/password/i), { target: { value: 'secret' } });
fireEvent.click(screen.getByRole('button', { name: /submit/i }));
expect(screen.getByText(/welcome, jane/i)).toBeInTheDocument();
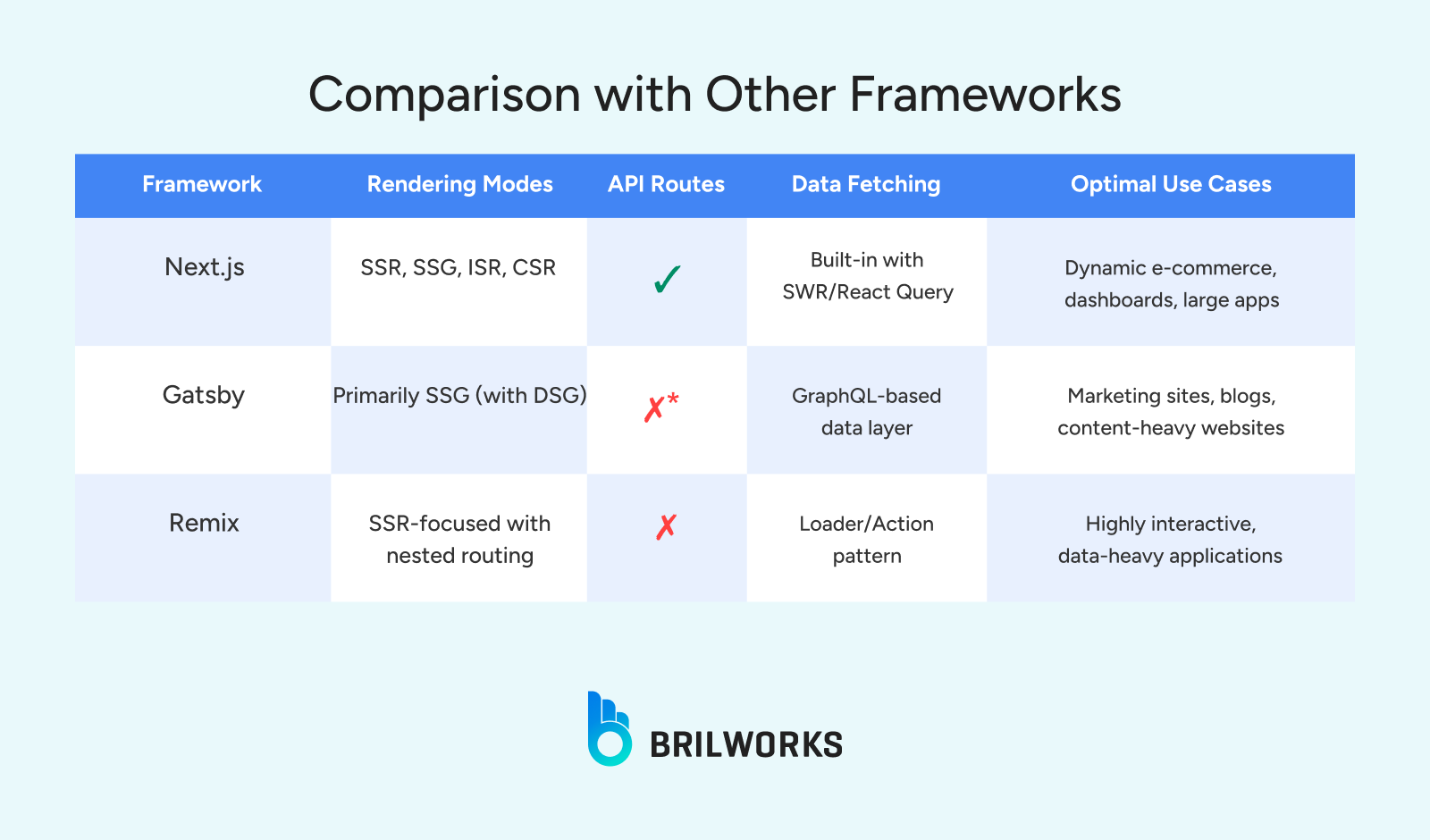
});Next.js extends React to include features like server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation (SSG), and built-in routing, while requiring minimal configuration.
Key features include:
Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Ensures dashboards, profiles, and dynamic content are always up to date.
Static Site Generation (SSG): Pre-build pages like product listings or blog posts for fast loading.
API Routes: Add backend functionality in pages/api/ without a separate server.
Gatsby also supports serverless APIs but lacks Next.js’s seamless integration.
Performance Optimization: Use memoization, useCallback, useMemo, and shallow component trees.
Type Safety with TypeScript: Gradually integrate TypeScript for strict typing, early error detection, and better productivity.
Documentation: Use Storybook for UI components, and maintain shared style guides and conventions.
CI/CD Pipelines: Automate testing, linting, formatting, and continuous deployment for reliable delivery.
Yes, using React Native you can target iOS and Android while reusing core React concepts like components, JSX, and hooks.
Advantages:
Cross-platform development saves time and effort.
Native performance using platform-specific UI components.
Reusable components across web and mobile.
Strong ecosystem and community support.
Applications like Facebook, Instagram, and Skype showcase React Native’s ability to build scalable, high-performance mobile apps.
Our team helps transform complex requirements into high-performing ReactJS apps. We:
Design feature-first project structures and choose suitable state management strategies.
Optimize performance using code splitting, memoization, and TypeScript.
Implement automated testing and CI/CD pipelines.
Extend applications to mobile with React Native while maintaining near-native performance.
Maintain clear documentation, monitoring, and ongoing support for reliability and scalability.
Whether launching a new product or scaling an existing platform, schedule a free consultation to build ReactJS applications that perform today and adapt for tomorrow.
ReactJS offers a component-based architecture, efficient rendering with the virtual DOM, and a rich ecosystem of tools that make it easier to manage and scale large applications.
Organizing your code by feature (rather than by file type), separating logic from UI, and using reusable components can help keep your application maintainable as it grows.
Not necessarily. While Redux is helpful for managing complex, global state, many smaller or medium-sized apps can scale well using the Context API and hooks like useReducer.
ReactJS itself is web-focused, but you can use your React skills with React Native to build high-performance mobile applications for iOS and Android.
Using code splitting (React.lazy, Suspense), memoization (useMemo, React.memo), TypeScript for type safety, and automated testing with Jest all contribute to a more performant and scalable app.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements