COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








When you first get a quote for outsourcing mobile app development, it generally covers the designing, coding, and basic testing. These quotes often leave out other costs that pop up later, such as third-party integration, maintenance costs, and so on. As a result, many businesses end up surprised by the real mobile app development cost. This is not uncommon; in fact, nearly half of app projects go over budget by 30 to 50%, as reported in a survey by BCG.
So the real “hidden costs” in outsourcing mobile app development are less about the technical tasks themselves and more about these organizational and leadership challenges. When these aren’t addressed early, outsourcing can quickly snowball into budget overruns and extended schedules.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through some of the hidden expenses associated with outsourced mobile development. We’ll share simple strategies to keep them in check. By the end, you’ll have a clearer idea of how to reduce app development costs.
Let’s start with some common hidden costs that can derail project development.
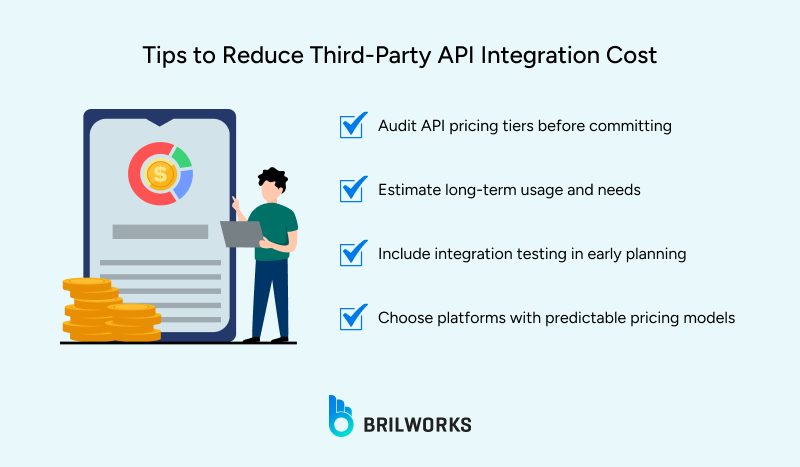
Many businesses focus on design and features, but forget about third-party integration costs. These add to the development cost. APIs like Google Maps and Mapbox have free options, but extra usage can cost money. In addition, Firebase Auth and Auth0 can add over $1,000/month for enterprise features. Not to mention, they can take even hundreds of hours to set up.
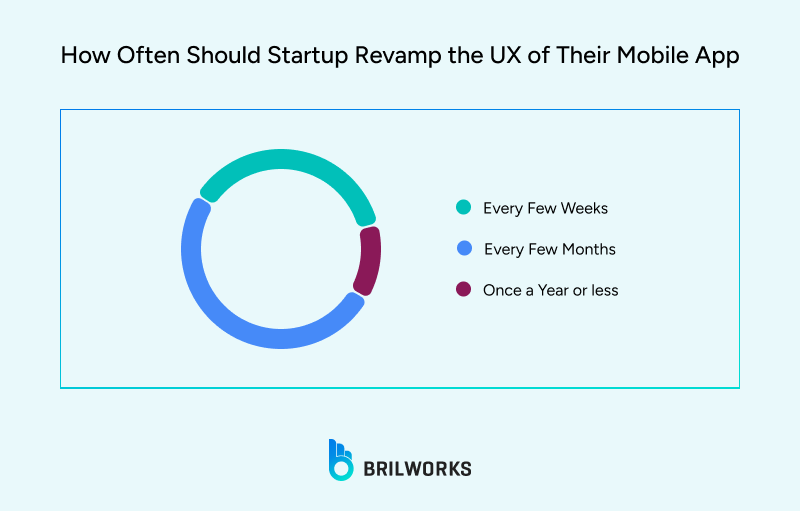
Design revisions can impact both timelines and budgets. Design rework is very common in mobile development. Over 50% of businesses revamp the UX of their mobile, as per the GoodFirms Survey 2025.
Quality assurance (QA) revisions can quietly become one of the most expensive parts of app development.
Involve QA early in the development cycle
Automate repetitive tasks like regression and smoke tests
Prioritize testing for high-impact areas like payment gateways or login flows.
Use continuous testing pipelines
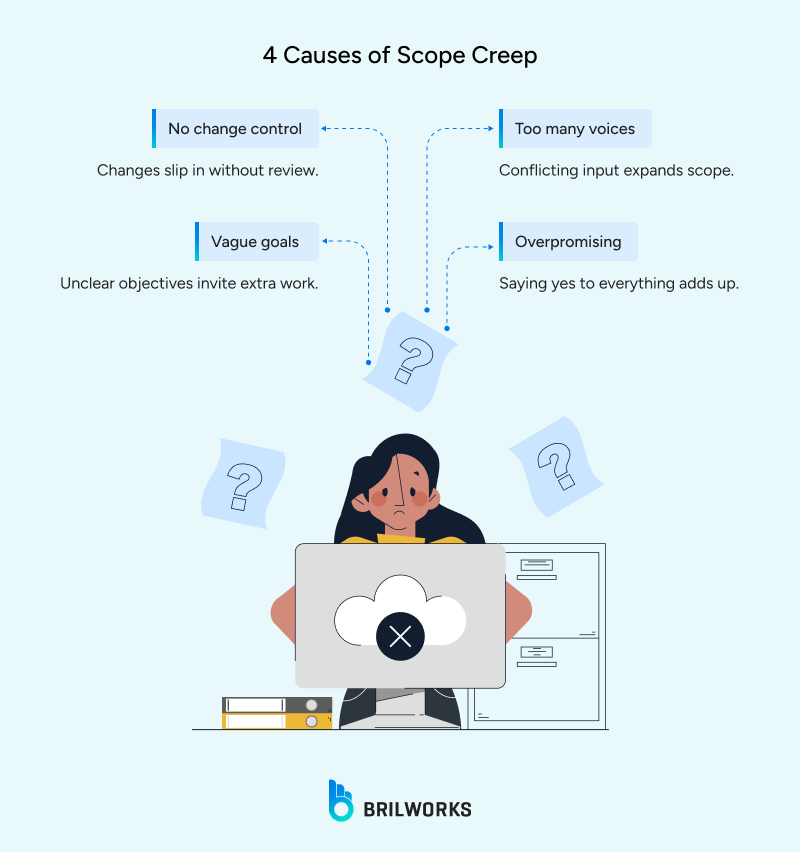
Scope creep is when the project grows beyond original objectives. In mobile application development, it usually starts with small enhancements, like, a new button here, an extra feature there, etc. Pretty quickly, there is a lot of additions. The real issue is not the extra work but the fact that there was little planning to support it.
To control it, teams must have a clear process for requesting changes, comprehensive documentation, and the discipline to say “not now” when the changes requested are no longer relevant to the current objectives.
Tips to Prevent Scope Creep:
Having clear, detailed requirements prior to writing any code is critical. Poor documentation is one of the top reasons outsourced app projects go south. Create a formal change management process. Here is how you can implement this.
Document every change request: Use a shared log or form
Assign ownership: One person or team should review and approve changes
Set review checkpoints: Weekly or milestone-based reviews help catch issues early
Get sign-off: No change moves forward without stakeholder approval
For each proposed change, assess:
Budget: Does it add new tools, licenses, or dev hours?
Timeline: Will it delay delivery or testing?
Functionality: Does it affect existing features or user flow?
Create a prioritization framework:
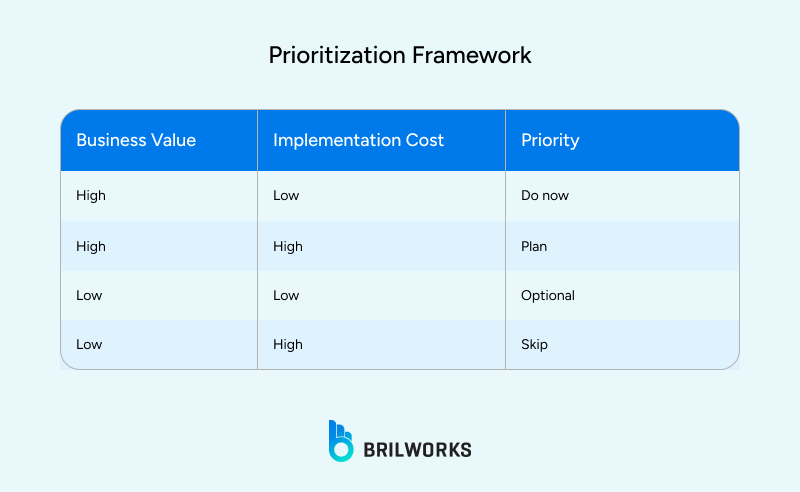
Prioritizing Features Through Value Assessment
You can use the MoSCoW framework to prioritize features. This simple method helps teams sort features into four buckets:
Must have: Core functions the app can’t launch without
Should have: Important, but not critical for first release
Could have: Nice-to-haves if time and budget allow
Won’t have: Ideas to park for future versions
For example, a social login might be a “Must have,” while dark mode could be a “Could have.”
Annual maintenance typically costs 15–25% of the initial development budget, according to Clutch and GoodFirms. For example, a $10k app may require $1.5-2.5k per year.
Real users behave unexpectedly, devices vary, and special cases occur that developers may never account for during testing, so even well-polished apps still require fixes after you've launched.
It is recommended to budget 10-20% of your initial development budget into a planning post-launch bug fixes and updates for the app. So with a $10k app, you will need $1k-$3k a year to account for bug fixes and updates. In particular, you will want this to cover:
Emergences patches
Emergency patches
OS compatibility updates
User-reported issues
Performance tuning
The better the initial quality assurance (QA), the fewer software defects manifested later. Even with rigorous testing, it is impossible to avoid all problems, since many problems appear only at scale.
The truth is, not having thorough QA to save upfront costs often leads to higher costs to fix bugs later, because quick development leads to weak codebases.
It’s a recurring investment. Operating system updates, new device releases, and third-party API changes all introduce shifts that can break functionality, disrupt UX, or trigger compliance issues.
For this, you can use a milestone-based payment structure in which payments are tied to specific, measurable deliverables. You only pay for progress and quality. Let’s understand it with an example:
Instead of paying for feature addition, you can specify exact requirements like "push notifications must trigger within 3 seconds" or "app must load in under 2 seconds on 4G." There can be several types of specific criteria. For testing, establish clear testing procedures:
Who will test (client, vendor, third-party)
How testing will be done (manual, automated, or using a device matrix)
According to a BCG survey of over 250 C-suite professionals, miscommunication was identified as one of the most common causes of project delays and cost overruns. A lack of clarity was found to be the primary reason for these delays.
One notable example is the DIA project, where the company faced a 16-month delay and incurred daily costs of $1.1 million while trying to implement an ambitious automated baggage system. This ultimately resulted in significant financial losses for the company.
When smaller organizations do not establish clear processes and communication strategies, it often results in unintended expenses because they overlook the importance of establishing standardized processes in the first place.
Below are the tools that you can use to keep everyone on the same page.
Jira, Trello for project management
Confluence, Notion for documentation repositories
Zoom, Google Meet for video conferencing
Requirements: Clear user stories, acceptance criteria, and scope boundaries
Decisions: Log who decided what, when, and why
Action items: Assign tasks with owners and deadlines
Instead of building the entire product at once, you can start with an MVP (Minimum Viable Product). An MVP allows you to test the market and understand audience behavior while keeping costs low. Developing an MVP is a common approach, especially for founders from non-technical backgrounds. You can check out our MVP development guide for startups to learn how to build one on a minimal budget. The guide also highlights the crucial role of choosing the right tech stack in the development process.
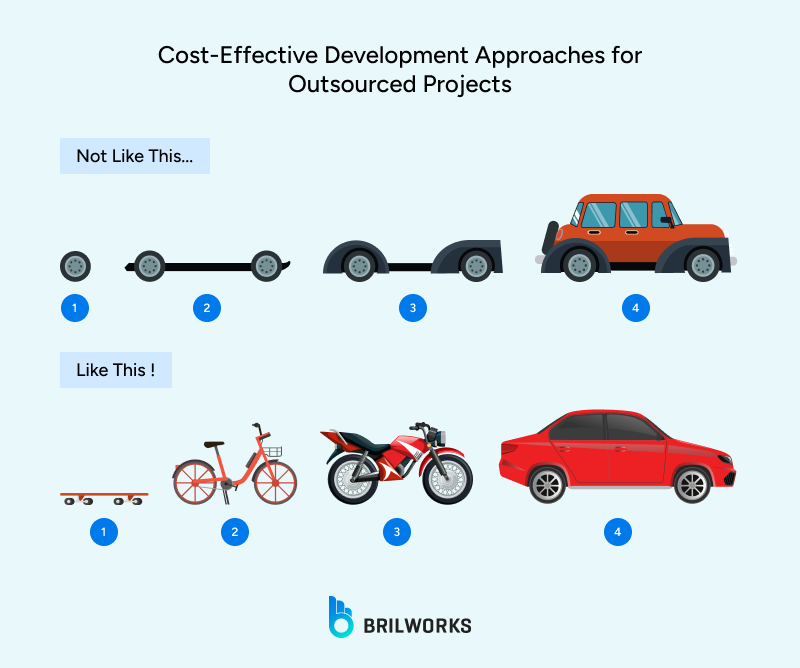
Cross-platform technologies like React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin can decrease development costs by as much as 40%. However, development costs are higher for native development. To find out more about cross-platform vs native development, look at our Native vs. Cross-Platform Development guide.
Cross-platform development allows you to build an app using one codebase, typically able to cover 80–90% of features, lessening the need to hire separate mobile development for both platforms. There can be a performance compromise, but applications such as Instagram, Google Ads, and Alibaba have built large parts of their apps using cross-platform technologies.
|
Framework |
Cost Benefit |
Performance Trade-offs |
Best Use Cases |
|
React Native |
30-40% savings |
Near-native performance |
Content-focused apps |
|
Flutter |
30-50% savings |
Excellent UI performance |
Visually rich applications |
|
Progressive Web Apps |
40-60% savings |
Limited native features |
Web-centric experiences |
Testing is an activity that is part of an iterative process rather than the end of the phase. While testing activities early in your development may increase your upfront costs 10-15% at the early stages, you will see the cost of bugs decrease roughly 60% in the late stages of development.
Outsourcing is most effective when approached with a partnership mentality. At Brilworks, we understand the challenges associated with outsourced application development, and we have refined our process to democratize access to development services while delivering results-based value. Schedule a free consultation to discuss how we can guide you through the complexity of application development at a budget you are comfortable with.
Outline the essential legal protections including NDAs, work-for-hire agreements, and IP assignment clauses that safeguard your app concept and code when working with external development teams.
Explain that annual maintenance typically costs 15-20% of the initial development investment, covering essential updates, bug fixes, and platform compatibility changes.
Describe the key verification methods including portfolio review, client references, technical assessments, and trial projects that help evaluate a development team's capabilities.
Compare fixed-price versus time-and-materials payment models, explaining when each is most appropriate and how they impact overall project costs and flexibility.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements